3D Printer Types: What Should You Choose?
2024-12-20 | By Antonio Velasco
3D Printing 3D Print Accessories 3D Printer
These days, I’m sure that you hear about 3D printing a lot. Whether it’s used in hobbyist projects or large-scale rockets (like Relativity Space is doing), it’s become an essential skill in any maker’s portfolio. Yet, getting into it seems pretty hard—there are tons and tons of options out there for a printer to buy! We’ll go over the types of 3D printers, how they work, and provide some tips to help you choose the right printer for you.
The Common Workhorse: Fused Deposition Modeling
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers, AKA Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) are the most common 3D printers. This is the type that you’ve probably seen around in people’s houses or DIY videos. These printers work by taking in a filament (often a thermoplastic string) and melting it to produce a malleable material. This melted material is then extruded to produce a model, layer by layer.
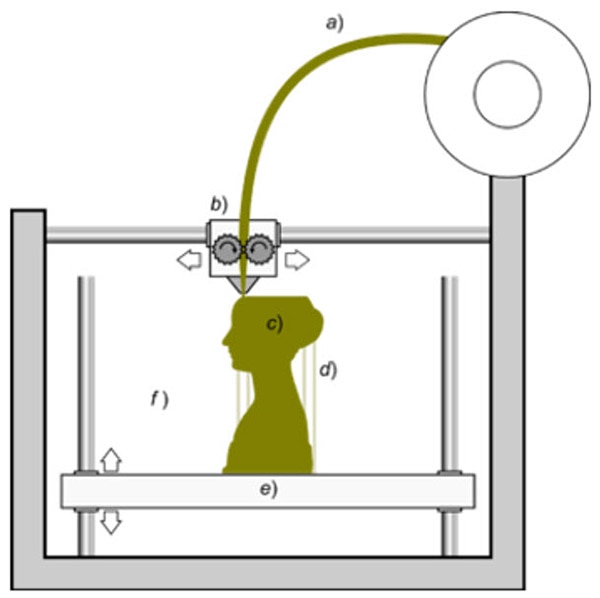
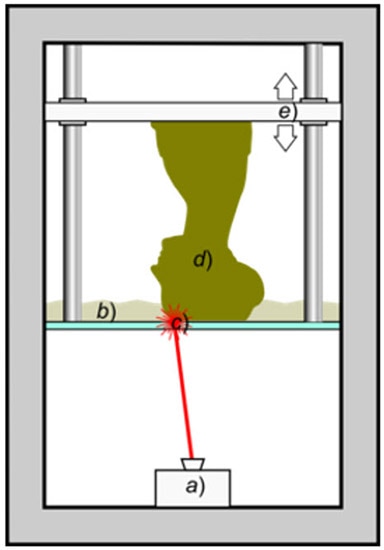
In this diagram, we can see how these printers work, with
a) the filament being melted
b) the extruder
c) the model
These printers are extremely affordable and easy to use, making them the ideal choice for the majority of hobbyists. They can utilize a variety of filaments, and range in price from a few hundred dollars up to several thousand. If you’re looking for something quick to learn and don’t require super fine precision, then FDM printers are for you!
Resin Printing: Producing Detailed Models
The next most popular 3D printers are Stereolithography (or SLA) printers. Instead of an extruder, these printers utilize a laser to cure specific portions of a liquid material into a solidified piece. You can think of it similarly to a focused beam cooling specific portions of water, creating ice shapes. Just in this case, it’s resin and a laser!
Since lasers can be very thin beams, they can create very intricate, precise details on your models. They’ve been used commercially to make dental models, prototypes, and more. Because of their unique properties (and difficulty to handle), these printers typically are more expensive, with the most basic being roughly $500 and high-end printers being several thousand. Furthermore, the cost of resin is much more than typical filaments for FDM printers. If you’re looking for high-precision or using it for a professional cause, and don’t mind paying the premium, then look for an SLA printer!
Digital Light Processing (DLP) printers utilize a similar process, but instead of a laser, make use of a light beam. This results in them being a bit faster to print but sacrificing some detail as light beams tend to be larger than laser beams. If you’re looking for a similar product with faster processing times, then look into DLP printers!
The Specialists: Industrial-Level Printing
Of course, for the previous printers, there are industrial equivalents for extremely precise and efficient printing. However, outside of resin and plastics, it’s possible to 3D print metal and ceramics! As I mentioned earlier, Relativity Space is creating 3D-printed rockets, and that’s only possible through some very specialized printers. The main types for this purpose are Selective Laser Sintering (or SLS), or specifically Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS). SLS and DMLS printers use a laser, like the SLA and DLP printers, but instead use it to fuse powdered materials (typically metal) to create solid objects. However, since the metal cannot be in a liquid form like resin can, the implementation becomes very complex very quickly, resulting in a very high price tag. Yet, the results are amazing, with tolerances as low as 0.001 inches! The lasers for these machines are typically only a few dozen microns long, only furthering how insane they are.
As a result, they’re mainly used for applications that require the ultimate precision, such as airplane parts or biomedical devices. These printers can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, but if you’re in the market to create such precise devices, there is no alternative.
Each printer has its specialties and usage, and it’s important to understand the different types that are out there—whether it's for a hobbyist or professional usage. Ensure that you evaluate your needs, budget, and overall skills in order to make an informed decision.
DigiKey offers a ton of 3D printer models and materials. Be sure to check them out!