Deep Dive into PCB Manufacturing: Fiber Laser Engraving
2024-11-25 | By Jake Hertz
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are central to all modern electronics, and advances in manufacturing techniques have opened new possibilities for creating more intricate, high-performance boards. One such method gaining popularity, especially for high-precision applications, is fiber laser engraving. The result is an efficient and accurate way to mark, cut, and pattern PCBs. We’ll explore how fiber laser engraving works and its benefits and challenges in PCB manufacturing.
What is Fiber Laser Engraving?
Fiber laser engraving is a process that uses a high-power laser beam to mark, engrave, or cut materials—primarily copper in the case of PCBs. The fiber laser emits a concentrated beam of light that can be focused to a fine point, which vaporizes the copper where it strikes. This enables precise material removal, allowing for intricate designs and component placement markings on the PCB surface.
Unlike other laser types, such as CO₂ or Nd lasers, fiber lasers amplify light through optical fibers that have been doped with rare-earth elements. This results in highly efficient energy use, creating a powerful and precise engraving tool that is ideal for delicate and high-density PCB designs.
The Fiber Laser Engraving Process
- Design Input: Similar to other PCB manufacturing processes, fiber laser engraving starts with a PCB layout designed using CAD software. This design is translated into machine-readable code that guides the laser’s movements.
- Laser Engraving: The fiber laser beam is directed onto the copper surface of the PCB, rapidly heating, and vaporizing the exposed copper. The laser follows the predetermined pattern with extreme precision, creating traces, component markings, or identification codes on the board.
- Layer-by-Layer Engraving: For multi-layer PCBs, fiber laser engraving can be used to selectively engrave specific layers or cut through individual layers without affecting the rest of the board. This level of control makes it ideal for producing complex boards with multiple signal paths and integrated components.
- Post-Engraving Processing: Once the engraving process is complete, the board may undergo additional steps like drilling, solder mask application, and assembly, depending on its final design and function.
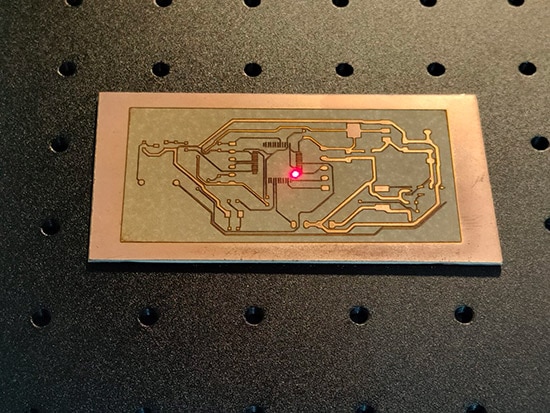 Fiber laser engraving a PCB.
Fiber laser engraving a PCB.
Why Choose Fiber Laser Engraving?
Among the many benefits of fiber laser engraving, its greatest advantage is its ability to handle intricate designs. This technique allows for extremely fine traces and detailed component layouts, as the laser's precision minimizes the risk of errors that could lead to signal loss or interference.
Another major advantage is that fiber laser engraving is a non-contact process. The laser does not physically touch the PCB, eliminating the risk of mechanical stress or damage to the board. Therefore, fiber laser engraving is preferable in manufacturing thinner or more delicate PCBs that traditional mechanical methods might otherwise damage.
Additionally, in terms of production efficiency, fiber lasers are incredibly fast, making them perfect for both rapid prototyping and large-scale production. The laser's high-power output and efficiency enable shorter processing times compared to milling or even other types of lasers without sacrificing precision.
Finally, fiber laser engraving eliminates the need for consumables like chemical etching solutions or milling bits. This reduces ongoing operational costs and makes the process more environmentally friendly, as there is no chemical waste to manage. While the upfront investment in fiber laser systems can be high, the long-term savings and sustainability benefits often outweigh these initial costs.
Challenges in Fiber Laser Engraving
While fiber laser engraving offers significant benefits, it is not without its challenges.
One limitation is the initial cost of fiber laser systems, which can be higher than other PCB fabrication equipment. For small operations, this upfront investment may be a barrier, although the long-term savings in consumables and maintenance often justify the expense.
Additionally, fiber laser engraving works best on relatively thin copper layers and is less suitable for boards that require thick copper traces. The vaporization process can also leave slight roughness at the edges of the engraved traces, which may require further processing or polishing for certain high-performance applications.
Conclusion
Fiber laser engraving is a cutting-edge approach to PCB manufacturing that provides manufacturers with unmatched precision, speed, and efficiency. While the upfront costs can be higher than traditional methods, the long-term benefits in terms of material savings, environmental impact, and production speed often make it a worthwhile investment for companies focused on high-precision applications. As PCBs continue to shrink in size and increase in complexity, fiber laser engraving will likely only gain a growing role in the future of electronics manufacturing.
Have questions or comments? Continue the conversation on TechForum, DigiKey's online community and technical resource.
















