How to Select the Right Motor for Your Application
2024-12-18 | By Jake Hertz
Selecting the right motor is necessary to ensure your application functions efficiently and reliably. Whether you are designing a robotic arm, an industrial conveyor system, or a small electric vehicle, the motor's characteristics will significantly impact the system’s performance. In this tutorial, we will break down the process of selecting the appropriate motor for your application by understanding motor types, key ratings, and using DigiKey's product filters to find the best match.
1. Define Your Application Requirements
Before diving into motor types and ratings, you need a thorough understanding of the operational conditions of your motor. Ask yourself the following:
- Load Type: What kind of load will the motor drive? Loads can be static (constant) or dynamic (varying). For example, a conveyor system requires consistent torque, while a robotic arm may need varying torque levels depending on the position and movement.
- Speed Requirements: How fast do you need the motor to spin? Applications like fans or pumps may operate at high speeds (thousands of RPM), while precision control applications like CNC machines may require slower speeds.
- Power Supply: Is your system DC or AC-powered? What voltage levels are available? The power source determines whether you need a motor rated for 12V, 24V, or 48V in DC systems or 110V, 230V, or higher in AC systems.
- Environmental Factors: Will the motor be exposed to high temperatures, moisture, or dust? Industrial settings may require motors with higher ingress protection (IP) ratings, while motors in outdoor environments need to withstand wide temperature ranges.
2. Understand Motor Types
Motor types vary significantly in construction, control methods, and suitable applications. Here's a detailed breakdown of the most common motor types and where they excel:
- Brushed DC Motors: These motors are simple and cost-effective, making them ideal for low-cost applications like hobby electronics, toys, or small robotics. However, they experience wear over time due to brush friction, making them less suitable for long-term continuous operation.
- Brushless DC Motors (BLDC): BLDC motors are highly efficient, offer long life, and provide precise control over speed and torque. They are commonly used in drones, electric vehicles, and industrial automation systems where minimal maintenance is required and performance is the priority. They require an electronic speed controller (ESC) to operate, which adds complexity.
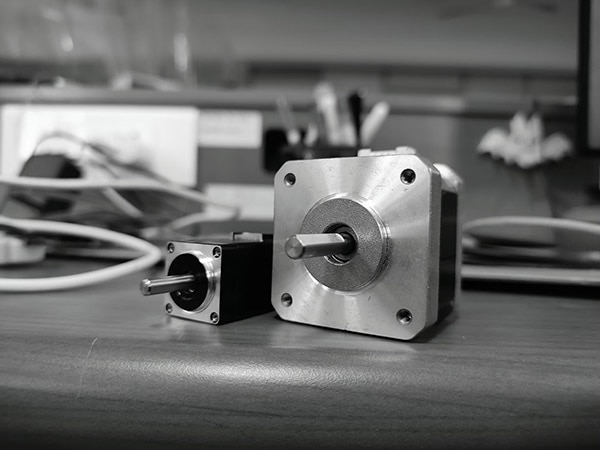
- Stepper Motors: These motors divide a full rotation into equal steps to provide excellent positioning accuracy. Stepper motors are typically used in 3D printers, CNC machines, and cameras. However, they lose torque at higher speeds and are not well-suited for high-RPM applications.
- AC Induction Motors: Owing to a combination of low cost, robustness, and high-power capabilities, these motors are widely used in industrial applications. Induction motors excel in applications such as pumps, fans, and conveyor belts. While highly reliable, their control is less precise than DC motors, especially at variable speeds, unless paired with a variable frequency drive (VFD).
- Servo Motors: Servo motors are designed to precisely control angular position, speed, and torque. They are typically used in robotic arms, CNC machinery, and automated systems requiring exact movement. Servo motors are often more expensive but provide feedback systems (like encoders) for high-precision control.
 Different types of motors.
Different types of motors.
3. Key Motor Ratings and Parameters
Once you’ve narrowed down the motor type that fits your application, the next step is understanding and comparing motor specifications. These parameters will help you fine-tune your selection to the exact motor that meets your requirements.
- Voltage Rating: Motors are designed to operate at specific voltages, and exceeding this can lead to overheating and failure. Standard voltage ratings include 12V, 24V, and 48V for DC motors and 110V or 230V for AC motors. Ensure your motor’s voltage matches your power source. For example, an electric vehicle often uses a 48V BLDC motor, while an industrial motor might run on 230V AC.
- Current Rating: Current draw is a notable factor, especially for battery-powered systems. A higher current rating indicates the motor consumes more power, which can strain your power supply or battery. You’ll need to ensure your power source can handle the motor’s maximum current under load. Check both the no-load and full-load current values for better estimation.
- Power Rating: Power (in watts) is needed to ensure that the motor can handle the work your application requires. This is typically calculated as voltage times current (P = V x I). For instance, a conveyor motor with a 500W rating will be suitable for moving moderate loads, while smaller applications like RC cars might need only 10W to 100W.
- Torque: Torque determines the motor’s ability to drive a load. It is expressed in Newton-meters (Nm) or ounce-inches (oz-in). Motors with higher torque ratings can handle heavier or more resistive loads. For example, a motor driving an industrial robotic arm requires higher torque to lift objects, whereas a fan motor requires less torque.
- Speed (RPM): Motors are rated in revolutions per minute (RPM). High-speed applications, like fans or grinders, require motors capable of thousands of RPM. Conversely, lower speeds are more appropriate for precision positioning (such as in robotic arms). Some applications may require both high speed and low speed, in which case a gear motor (motor combined with a gearbox) is recommended.
 Waveforms for a sinusoidally controlled BLDC motor.
Waveforms for a sinusoidally controlled BLDC motor.
4. Leveraging DigiKey’s Product Filters
Once you’ve established the motor requirements, you can utilize DigiKey’s extensive product catalog to narrow down potential motor candidates. DigiKey’s filter system allows you to set specific parameters that match your design requirements.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: DigiKey offers operating voltage and current draw filters. Select a motor that fits within your power source's voltage and current limits. For example, use the voltage filter to narrow down motors rated for 12V or 24V if you’re working with a typical DC supply.
- Motor Type: Depending on your application, you can easily choose between different motor types, such as DC, BLDC, stepper, AC induction, or servo motors.
- Speed and Torque: For applications with specific performance needs, use the RPM and torque filters to zero in on motors that match your required speed and load-handling capacity.
- Mounting Type and Size: You can filter motors based on their physical size, weight, and mounting type. This is important if your design has limited space or if the motor must fit into a pre-defined housing or system.
- Environmental Ratings: If your application operates in harsh environments, you can filter by IP ratings to find motors that offer protection against dust and moisture.
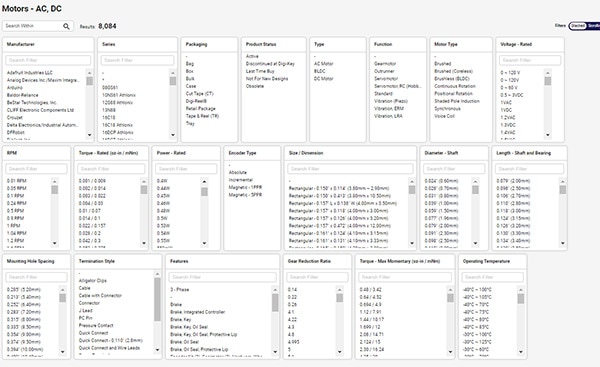 Motor filters on the DigiKey website.
Motor filters on the DigiKey website.
5. Additional Considerations
- Motor Controllers: Many motors, especially BLDC and stepper motors, require motor controllers to function correctly. These controllers handle speed, torque, and direction and often allow for more precise control of motor parameters. Be sure to select an appropriate controller that is compatible with your motor.
- Thermal Management: Heat dissipation is prominent for motors, especially in high-power or continuous-duty applications. Consider motors with integrated cooling features or design your system to include additional cooling measures like heatsinks or fans.
- Cost vs. Performance: High-performance motors can handle demanding applications but often have a higher price tag. Balance the motor's performance with your budget. Sometimes, a less expensive option with additional gearing or external control can meet the performance requirements without needing a high-end motor.
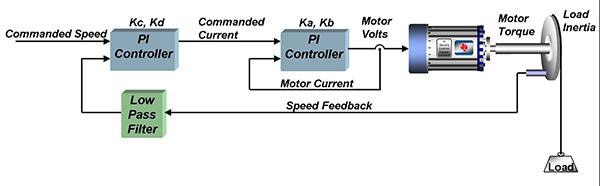 A motor control circuit.
A motor control circuit.
Conclusion
Selecting the right motor for your application involves careful consideration of load requirements, motor types, and critical ratings such as voltage, current, power, torque, and speed. DigiKey’s product filters can streamline the selection process and help you find a motor that fits your exact specifications. Whether you need precision control, high torque, or energy efficiency, understanding the parameters of each motor guarantees that your design performs optimally with minimal issues down the line.