What is a TRIAC-Triode Alternating Current?
2024-11-25 | By DWARAKAN RAMANATHAN
What is a TRIAC?
TRIAC can be expanded as a Triode Alternating Current. TRIAC is used to control AC power because once turned on, a TRIAC can conduct in both directions, unlike other transistors like MOSFET or IGBT. The TRIAC is a three-terminal semiconductor switching device that includes a Main Terminal 1, Main Terminal 2, and a gate Terminal. They can conduct in both the conditions of the gate signal, positive and negative. A TRIAC is a simple switching device that can work on an AC gate signal, unlike other transistors, because a TRIAC is made by combining two transistors and connecting their gate terminals. The basic structure of the TRIAC can be understood by looking at the below figure.
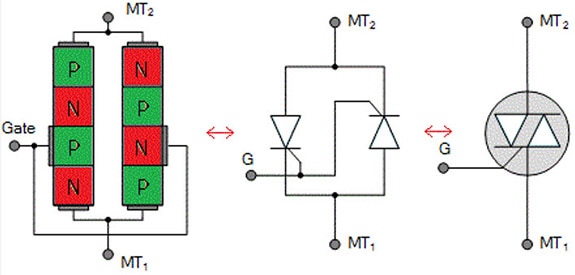
The Figure shows the Physical Construction of the TRIAC(Left), Two Transistor Analogy(Middle), TRIAC Symbol(Right)
BT136-TRIAC
This is a commercial TRIAC that is used widely in many circuits to control the switching operation using an alternating current or alternating gate signal. This is a bidirectional device.
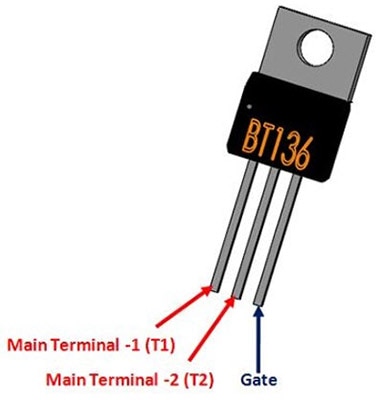
The above figure shows the terminals of a BT136 IC
Operation of a TRIAC
A TRIAC can go to a conduction state if the applied voltage is equal to the breakdown voltage, but the most preferred way of turning on a TRIAC is by providing a gate pulse, either positive or negative.
Four operating modes of a TRIAC are:
- MT2 is positive with respect to MT1 with a gate polarity positive
- MT2 is positive with respect to MT1 with a gate polarity negative
- MT2 is negative with respect to MT1 with a gate polarity negative
- MT2 is negative with respect to MT1 with a gate polarity positive
Voltage vs Current Characteristics of a TRIAC:
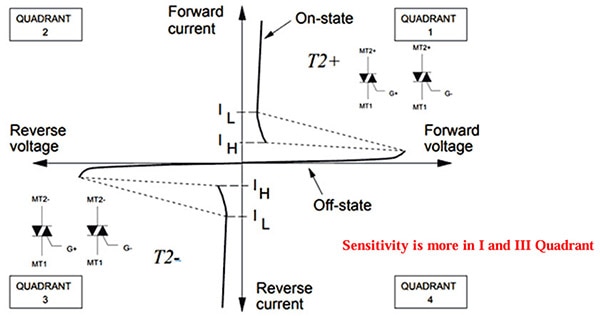
First Quadrant Operation of TRIAC: The voltage at terminal MT2 is positive with respect to terminal MT1, and the gate voltage is also positive with respect to terminal MT1.
Second Quadrant Operation of TRIAC: The voltage at terminal MT2 is positive with respect to terminal MT1, and the gate voltage is negative with respect to terminal MT1.
Third Quadrant Operation of TRIAC: The voltage of terminal MT1 is positive with respect to terminal MT2, and the gate voltage is negative.
Fourth Quadrant Operation of TRIAC: The voltage of terminal MT2 is negative with respect to terminal MT1, and the gate voltage is positive.
Advantages of TRIAC
It can be triggered with positive or negative polarity gate pulses. It requires only a single heat sink of a slightly larger size. It requires a single fuse (current rating depends on the size of the TRIAC) for protection. A safe breakdown in either direction is possible.
Disadvantages of TRIAC
They are not very reliable compared to other Switching devices like an SCR. It has a (dv/dt) rating lower than other switching devices like MOSFETs and SCRs. We need to be careful about the triggering circuit (the circuit that generates the gate signal), as it can be triggered in either direction.
Uses of TRIAC
TRIAC's purpose is to control the electrical power in AC circuits. They are used in light dimmers to adjust the brilliance of a bulb and to adjust the speed of motor appliances like fans and blenders. TRIACs are also employed in controlling heaters, for thermosetting the temperature. They are essential because they can handle quite high voltage and current ratings; thus, they find a lot of applications in power control jobs.
Conclusion:
TRIACs today form the electronic backbone in the efficient and reliable controlling of AC power in very diversified applications. From light dimming or just simple speed changing of motors to systems that regulate heat, TRIACs play a vital role in boosting functionality and efficiency in many everyday devices. Since they can handle large voltages and currents, they are quite indispensable in both household and industrial applications.















 中国
中国