Diodes...In Transistors?
2023-12-08 | By Antonio Velasco
Before we dive into the fascinating world of MOSFET transistors, let's rewind and revisit the humble diode. Diodes are simple semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the other. But what if I told you that within every MOSFET, two diodes are secretly at play?
What is a MOSFET?
A MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) consists of three terminals: source (S), gate (G), and drain (D). The magic begins when we examine the two PN junctions within the MOSFET, akin to two diodes operating in concert.
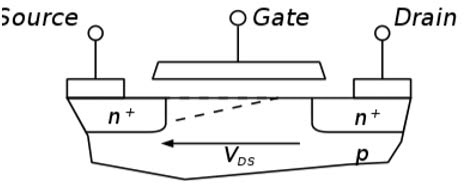
Imagine a MOSFET in its off-state, where the gate-source voltage (Vgs) is below the threshold to turn it on. Here, a diode-like structure forms between the source (S) and the body of the transistor (also known as the substrate). Current can flow from S to the body (N to P), but not the other way around. It's essentially a diode, allowing one-way electron traffic.
Now, consider the drain (D) and the body, which also form a diode-like junction. Similar to the source-body diode, this junction permits current flow from D to the body (P to N) when the transistor is off. However, it blocks the reverse flow.
Here's where the diode duality takes center stage!
When we apply a positive voltage to the gate terminal (Vgs), it creates an electric field that allows current to flow from the source to the drain. This forward biasing of the source-body diode resembles turning on a regular diode. It conducts and allows the main current to flow.

Conversely, if the gate voltage is low (Vgs < threshold), the source-body diode remains in its reverse-biased state, acting like an off diode. It blocks the flow of current from source to drain.
Now, let's witness this dual-diode action in MOSFETs in practical terms. Much like diodes, MOSFETs are employed for signal amplification and switching tasks. They serve as electronic gates, controlling the flow of current. However, unlike diodes, they offer finer control through voltage manipulation.
While diodes are all about one-way current flow, MOSFETs go beyond. They introduce voltage control, allowing you to fine-tune the flow of electrons at a high level of precision. This voltage-controlled feature opens the doors to amplifiers, digital logic gates, and so much more. You can also use them for safety purposes as they can protect circuits from voltage spikes in a similar fashion to diodes.
Practical Applications
One of the most common uses of MOSFETs is in power amplification. By modulating the gate voltage, MOSFETs can control the flow of current between the source and drain, amplifying weak signals into powerful output signals. This is a component feature commonly known as amplifiers, especially at the microelectronics level.
MOSFETs are fundamental building blocks in digital circuits. They serve as switches in logic gates, enabling the creation of complex digital systems. N-channel and P-channel MOSFETs are combined to construct complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) circuits, which are energy-efficient and widely used in microprocessors, memory devices, and digital signal processors.
MOSFETs are also key components in voltage regulator circuits, ensuring a constant (and stable!) voltage output from power supplies. They are often used in conjunction with feedback control systems to maintain precise voltage levels for various electronic devices.
MOSFETs are integral to PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation, a technique for motor control and whatnot) circuits, rapidly switching on and off to regulate the average power delivered to the load, achieving precise control.
In closing, MOSFETs can be simply described as diodes with a little twist. Their PN junctions operate like a diode and enable them to work as switches or amplifiers. The addition of voltage control to diode properties opens up a world of possibilities.
See my first article on Demystifying the Diode!
Or my follow-up article on Zener Diodes: Zener Diodes - The Voltage Police!
Or my next article on Light Emitting Diodes: Shining Some Light on LEDs!

Have questions or comments? Continue the conversation on TechForum, DigiKey's online community and technical resource.
Visit TechForum










 中国
中国