Zener Diodes - The Voltage Police!
2023-12-08 | By Antonio Velasco
A Zener diode is a type of semiconductor diode that is designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region of its voltage-current characteristic curve, called the "Zener breakdown." Unlike regular diodes, which are primarily used to allow current to flow in one direction (forward bias) and block it in the other direction (reverse bias), Zener diodes are specifically designed to maintain a constant voltage across their terminals when they are operated in reverse bias. Before we unwrap the magic of Zener diodes, let's have a quick chat about the PN junction. You see, at the heart of every diode, including our star Zener, lies this remarkable interface.
Imagine a junction of P (positive) and N (negative) semiconductor materials, each with its unique charge characteristics. When you apply a forward voltage across the diode (positive to P, negative to N), it's like opening the floodgates for electrons to flow from the N-side to the P-side. In this state, diodes are happy to oblige, allowing current to pass through. However, if you reverse the polarity, things get interesting. Regular diodes will withstand a small reverse voltage, but beyond a certain threshold, they break down like a flimsy bridge under heavy traffic -- enter the Zener Voltage.
Now, let's talk about that threshold - the Zener voltage. It's the secret ingredient in Zener diodes, the voltage at which they say, "Okay, enough is enough; I'm breaking the rules." Each Zener diode is engineered to have this Zener voltage nailed down to a specific value. When you apply a reverse voltage equal to or higher than this Zener voltage, the diode doesn't just fail; it works its magic. See the I-V curve below for a practical graphical representation.
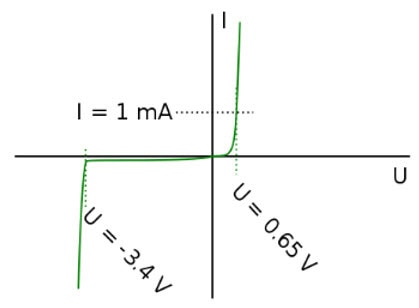
This is where the device physics gets exciting. When you crank up the reverse voltage, something called the "Zener effect" kicks in. Electrons in the N-side, like rebellious teens, gain enough energy from the electric field and break free, creating electron-hole pairs. These newly liberated electrons, on a collision course with destiny, knock more electrons loose. It's like a cascade of rebellion. Electrons gain energy, collide, and liberate others in a chain reaction. This controlled chaos results in a sudden, predictable increase in current flowing through the diode, while the voltage across it remains constant, thus creating a regulator.
What Can I Use the Zener Diode For?
Zener Diodes are typically used in the industry as regulators or references for voltages. Especially across small circuits, they’re perfect for ensuring the safety of multiple components.
Zener diodes are typically used for stabilizing voltages in DC circuits. They keep the voltage steady and stable regardless of what fluctuations may occur.
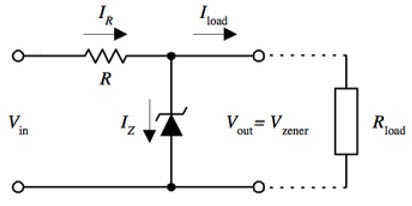
Here’s an example of a circuit from Wikipedia displaying a linear regulator. You can see that, in between, it will regulate the voltage through the load current.
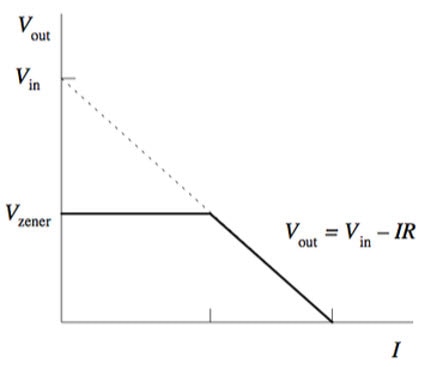
You can see here that, even if the voltage wants to be higher, it won't because of the Zener Diode.
Similarly, in AC circuits, Zener diodes can limit the peak voltage of signals, preventing damage to sensitive components.
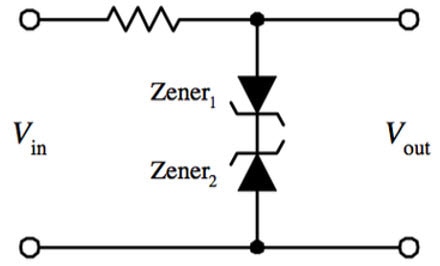
Here’s Wikipedia’s circuit example for a waveform clipper, displaying two Zener diodes next to each other in series that can modify signals and as previously mentioned, limit peak voltages. It does exactly as the name suggests: clip waves.
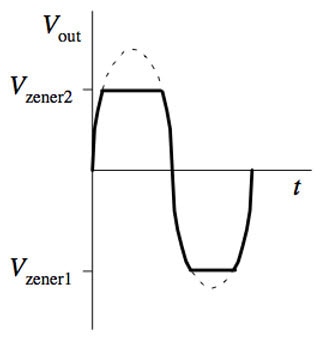
You can see in this graph exactly where the waveform is "clipped" from the Zener Diodes. You need two for each part, and it allows your AC voltage to be limited.
The Zener diode acts as an essential component for anything from a power supply to protecting sensitive components. Although small, its voltage-regulating magic is extremely useful. There are a lot of things that diodes can do, and if you’re interested in reading more about them, check out the other diode articles below!

Have questions or comments? Continue the conversation on TechForum, DigiKey's online community and technical resource.
Visit TechForum










 中国
中国