Electric Switch/Electromechanical Relay AC vs DC Ratings
2023-08-23 | By Don Wilcher
Within your maker projects, you’ll eventually need an electric switch or an electromechanical relay. This project can involve building a 3D printer from scratch or using a construction kit to assemble a mobile robot like the XRP. The primary component shared between these projects is the use of switching contacts enabling the interruption or flow of an electrical current within a circuit. Although contact ratings might not seem initially important for the selection or replacement of an electromechanical component, understanding the contact rating is vital. We’ll explore the similarities and differences between AC and DC contact ratings of electric switches and electromechanical relays. But prior to discussing the contact ratings, we’ll begin with a review of the electric switch and electromechanical relay basics.
Electric Switch Basics
An electric switch uses switching contacts to open or close a circuit, allowing or preventing the flow of electricity. The contacts are actuated by a mechanically activated plunger or lever. When the switch is turned on, the contacts close, and electricity flows to the load, such as a light bulb, LED, solenoid, or DC motor. When the switch is turned off, the contacts open, and electricity stops flowing to the load. The user can turn the switch on or off by pressing the operator, which is the plastic button on the plunger or lever.
 A Typical Emergency Stop Electric Switch with an attached Operator.
A Typical Emergency Stop Electric Switch with an attached Operator.
Electromechanical Relay Basics
An electromechanical relay is a switch that uses an electromagnet to open or close a circuit. When electricity flows through the coil of the relay, it creates a magnetic field that attracts a metal arm called the armature. This arm then closes the switch contacts that allow current to flow through the load. When the power is turned off, the magnetic field disappears, and the armature springs back to its original position, opening the contacts and turning off the load. An electric switch can be used to turn the power on and off to the relay coil.
In simpler terms, an electromechanical relay is a switch that can be turned on or off by electricity. It is used to control electrical circuits by opening or closing them.
 An electromechanical relay and wiring diagram.
An electromechanical relay and wiring diagram.
The Nature of Electrical Current
The difference between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) is the direction of the current flow. AC current switches direction periodically, while DC current flows in one direction only. This difference affects the behavior of electrical parameters such as voltage, voltage spikes, and transients. These parameters interact with electromechanical relays and electric switching contacts during operation. An important aspect of electrical current behavior during contact switching is the occurrence of contact arcing. The following items highlight the differences between AC and DC contact ratings and their relevance.
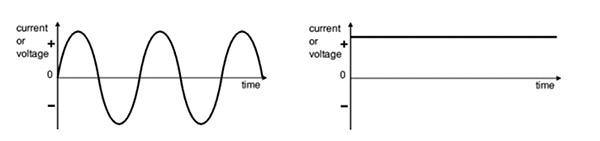 AC and DC Voltage signals.
AC and DC Voltage signals.
Contact Arc
Switching contacts experience an arc due to the electrical discharge that occurs during the separation or joining of conductive surfaces. Contact arc produces heat, and the intensity of the arc depends on the current characteristics being switched in either an AC or DC circuit. In an AC circuit, the arc is short-lived due to the alternation cycles of the voltage’s sinewave signal. The arc is then extinguished by the voltage sinewave signal crossing the zero axis. In a DC circuit, however, the constant voltage level allows the arc to persist. With DC voltage, there is no transition to ground. Instead, this transition exists when the power supply is turned off or removed from the DC circuit. Therefore, the arc is more intensive in a DC circuit rather than an AC circuit, resulting in higher levels of switch contact wear.
 Switch contact wear due to arcing.
Switch contact wear due to arcing.
Voltage and Current Levels
The voltage and current levels in AC and DC circuits vary greatly, depending on the contact switching application. The circuit's operation will vary depending on the electromechanical relay and electric switch contact ratings. The switch contact ratings must be considered to ensure the proper functioning of the switching control application. In AC switching control applications, voltage and current ratings are typically specified as Root Mean Square (RMS). RMS is a well-established parameter in the electrical industry that is used to specify AC power supply requirements and represents the effective or equivalent values of AC voltage and current.
In contrast, DC ratings reflect the continuous or peak AC voltage and current values. As a result, an electromechanical relay or electric switch rated for a specific AC voltage and current may not be compatible with the same DC voltage and current. This mismatch occurs due to the difference between continuous peak voltage and current, which do not align with an electrical circuit's steady-state operating voltage and current values. As a result, selecting the appropriate contact ratings is critical for maintaining the proper operation of electrical or electronic circuits.
Loads: Inductive and Capacitive
Inductive and capacitive loads can affect the contact-switching operation in electrical circuits. Inductive loads such as motors, solenoids, and transformers can generate voltage spikes or back Electromotive Force (EMF) when the circuit is interrupted using an electromechanical relay or electric switch. These switching devices can handle such transients in an AC circuit or system using suppression devices like a resistor-capacitor (snubber) circuit. With the AC signal crossing the zero axis, the transient is extinguished. In a DC circuit/system or capacitive loads such as electronic circuits and capacitors, transients behave differently. Therefore, contact switching suppression ratings differ in a DC circuit or system and must be uniquely designed and managed. You must also choose contact ratings appropriately, based on the load and circuit or systems voltage power supply requirements (AC or DC).
 Inductive and Capacitive load examples.
Inductive and Capacitive load examples.
Final Considerations
Consider these items when selecting electromechanical relays and electric switches for AC and DC circuits and systems.
- The switching speed of an electromechanical relay and electrical switch is important to consider for the contact rating. AC circuits typically have a higher switching speed than DC circuits due to AC changing direction or alternating around the zero axis. This alternating movement allows the electric switch or electromechanical relay to open and close faster than the constant DC circuit.
- The electromechanical relay and the electrical switch arcing distance must be considered in an AC or DC circuit. The arcing distance is the distance between the electrical switch or electromechanical relay contacts, and AC circuits typically require a larger arcing distance than DC circuits. Therefore, DC rating switching contacts are inappropriate for AC circuit applications due to the arcing distance switch contact design. AC switch contacts can extinguish the arc better than the DC switching device — a result of the signal crossing the zero axis.
Considering the distinctions in AC and DC circuits, systems, and load characteristics, you can properly select the appropriate electromechanical relay and electrical switch for your next project.
Recommended Reading
What is the Difference in AC vs DC Current? – ATM Quick Take | DigiKey
What is Back EMF in DC Motors? - Another Teaching Moment | DigiKey
Relay Basics - Another Teaching Moment | DigiKey Electronics
How to Choose a Relay - Another Teaching Moment | DigiKey Electronics
Switch Basics - Another Teaching Moment | DigiKey Electronics
Have questions or comments? Continue the conversation on TechForum, DigiKey's online community and technical resource.













