What is a Voltage Regulator?
2020-07-01 | By Maker.io Staff
All electronic devices are designated to run at predetermined power ratings, i.e. voltage and current. While current consumption is dynamic and depends on the device load, the voltage supply is fixed and ideally constant for the proper functioning of the device. A voltage regulator is responsible to maintain this ideal voltage needed for the device. Your laptop, wall charger, and coffee maker all have voltage regulators.
In this blog, we’ll look more closely at the concept of a voltage regulator and its various types, and we’ll elaborate on the common voltage regulator ICs and their common applications!
What is a voltage regulator?
The power supply unit of an electronic device converts incoming power into the desired type (AC-DC or DC-AC) and desired voltage/current characteristics. A voltage regulator is a component of the power supply unit that ensures a steady constant voltage supply through all operational conditions. It regulates voltage during power fluctuations and variations in loads. It can regulate AC as well as DC voltages.

SMPS and a wall charger - both have an onboard voltage regulator (Image source: TDK Lambda (left) and Triad Magnetics (right))
A voltage regulator usually takes in higher input voltage and emits a lower, more stable output voltage. Their secondary use is also to protect the circuit against voltage spikes that can potentially damage/fry them.
Different types of voltage regulators
Voltage regulators used in low-voltage electronic devices are usually integrated circuits. Power distribution centers providing AC power to residential and industrial consumers use more sophisticated and mechanically large voltage regulators that maintain rated 110 V (US household standards) voltage regardless of consumption demands across the area.
Based on the physical design, voltage regulators can be seen in integrated circuits, electromechanical devices, or solid-state automatic regulators. The most common classifications of the active voltage regulators (that use amplifying components like transistors or op-amps) are linear and switching regulators.
Linear regulators are simple transistor-based devices usually packaged as ICs. Their internal circuitry uses differential amplifiers to control output voltage against a reference voltage. Linear voltage regulators may implement fixed output or have an adjustable control. They typically need input current comparable to the output current.
Switching regulators toggle a series device ON/OFF at high frequency, varying the duty cycle of voltage transferred as output. Their common topologies are buck, boost, and buck-boost. Buck converters are more efficient during voltage step down and are still capable of stepping up the output current. Boost converters, like the TPS6125 from Texas Instruments (TI), can step up the output voltage to more than the input voltage.
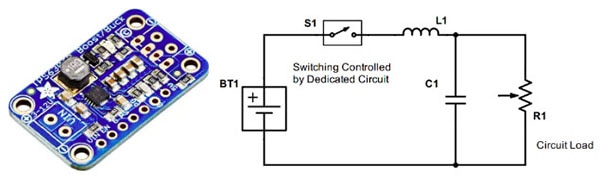
Adafruit’s Buck-Boost Converter with TI’s TPS63060 onboard and a Switching Regulator Circuit (Image source: Adafruit Industries (left) & DigiKey SchemeIt (right))
Linear voltage regulator integrated circuits
The most common DC linear fixed voltage regulator ICs used in electronic circuits are the 78XX and 79XX series for positive and negative voltage output respectively. The XX stands for the output voltage which ranges from 2.5 V to 35 V and can support up to 2 A of current. They are available in surface-mount, TO-3, and TO-220 packaging. They have three connection pins, an input, a common GND, and an output pin. Voltage regulator modules are also available commercially.
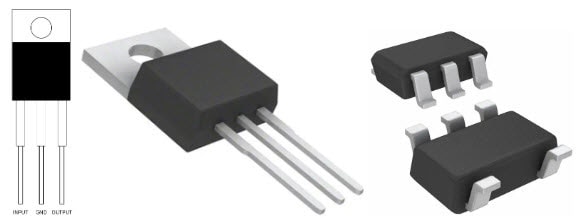
Different Packaging for the 7805 IC family.
An STMicroelectronics LM7805 gives +5 V voltage across the output and GND terminal while TI’s LM7912 gives -12 V output. The negative voltages are only a relative reference with respect to the GND terminal.
Linear voltage regulators are low-cost, and easy-to-use ICs with very low electromagnetic interference, and quick-response to voltage fluctuations. While they are useful for simple applications, there are a few drawbacks to using them.
- The 78XX and 79XX ICs can provide constant and rated output voltage only if the input voltage is at least 2.5 V or more than the output. For example, you can’t obtain a 9 V output from an LM7809 IC if it is powered by a 9 V Li-Ion battery.
- The voltage drop happens because these ICs essentially behave as pseudo-resistors and release the extra input battery power as heat. This is inefficient, and the heat needs to be dissipated using heat sinks or fans. High-voltage high-current ICs need large heat sinks or continuous fan use to ensure stable temperature ranges. High input voltages for low outputs, like a 24 V input to an LM7805, have a very poor efficiency of 20%.
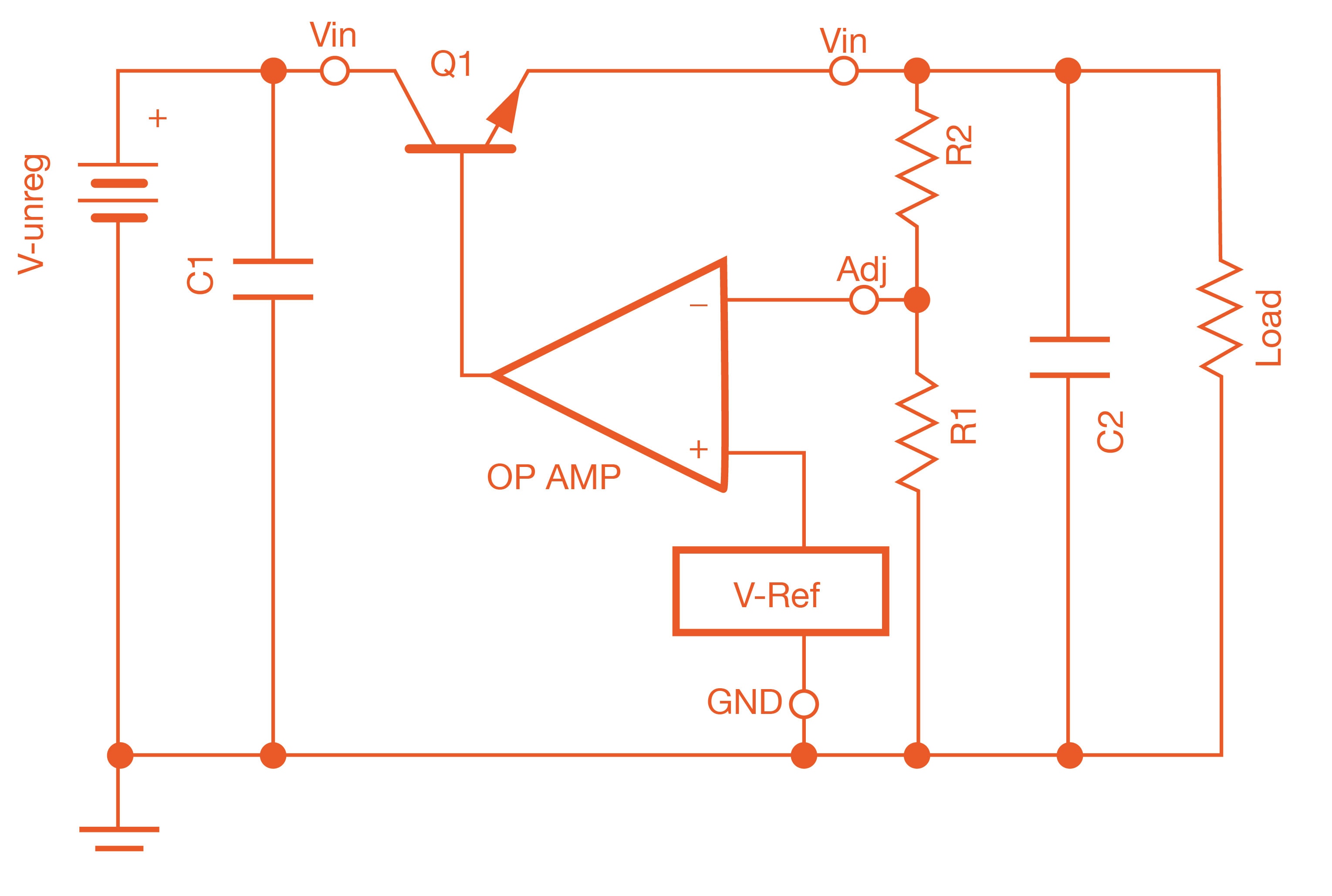
TI’s LM317 is a DC linear adjustable voltage regulator that allows modifying the output voltage based on an external R1/R2 voltage divider principle using resistors. It is easy to use and needs two resistors as shown. It can provide up to 1.5 A current over a positive voltage range of 1.25 V to 37 V. Other variants of the LM317 IC family, LM317L and LM317M provide 100 mA and 500 mA current respectively.
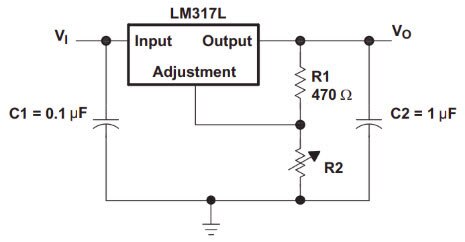
LM317 IC Family Schematic (Image source: Product Datasheet from Texas Instruments)
Applications of voltage regulators
- Positive and negative voltage regulators can be used together to power sensors, op-amps, and other electronic modules that need both voltages.
- All common microcontroller development boards, like those from Arduino and Raspberry Pi, can be powered using the LM7805 output to the 5 V pin. Arduino boards also have an onboard low-dropout voltage regulator like On Semiconductor’s NCP1117S to regulate power input coming from the barrel jack or Vin.
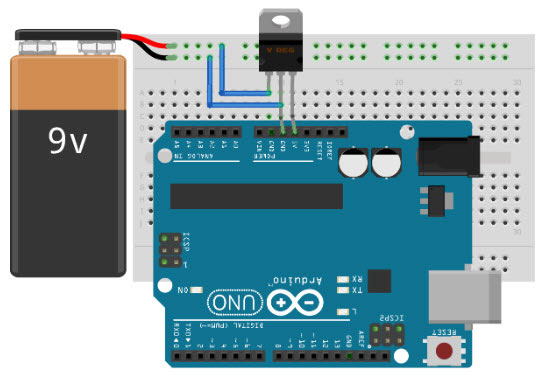
An LM7805 externally powering an Arduino (Image source: Maker.io)
Voltage regulators are one of the most important components of an electronic circuit. They are responsible for its safe and consistent functioning. Extremely high voltage regulators use power electronics circuits with high power ratings in industrial settings on heavy machinery.
Recommended Reading
What is a Voltage Regulator Another Teaching Moment | DigiKey