目录
返回顶部
Matter
Matter Boards
Thread Boards
Cellular / Mobile
Performance Levels
Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) Cards and Data Plans
Antennas
Transceivers, Gateways, and Routers
Network Protocols
Wireless Personal Area Networking (WPAN)
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
Cellular
Low-Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN)
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
Interference
Certification and Testing
Dealing with interference
Wireless Transceivers
Form Factors of Transceivers
Antennas
Antenna Integration
External Antenna
Internal Antenna
Antenna Terminology
Popular Antenna Types
Micro Strip Calculator
dBm To Milliwatt Converter
Products
Services
Wireless
Radio Frequency (RF) products are focused on Wireless communication. Within Wireless there are some common topics that will apply across a broad range of product categories (for example Matter, Cellular, Network Protocols, Interference, and Security). In the product categories of Wireless some of the first places to get started are Transceivers, and Antennas.
Wireless communication, a foundational technology enabling information transmission without physical connections, has revolutionized modern interactions and driven the growth of the Internet, media streaming, and more. eMagazine on wireless technology.
Matter
Matter is a wireless connectivity standard designed to make it easy for home automation and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to connect, communicate, and operate across different manufacturers and/or network protocols. Matter is developed and maintained by the by the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA), which was previously known as the ZigBee Alliance and headed up by companies including Apple, Amazon, and Google. Matter can run on Wi-Fi and Thread devices, with a broad compatibility that removes the complexity between multiple smart home platforms.
 The Matter Logo found on Matter Compatible devices, Provided by CSA
The Matter Logo found on Matter Compatible devices, Provided by CSA
What problems does Matter fix? View Answer
Prior to the introduction of Matter, the smart home automation market was fragmented with Amazon Alexa, Apple HomeKit, Google Home, and Samsung SmartThings having their own wireless network standards. To bridge this fragmentated smart home ecosystem the CSA developed a new interoperating framework for all manufactures to work under.
The Matter Version 1 specification is only for simple devices such light bulbs, switches, locks, home heating, ventilation and air conditioning controllers and home entertainment. Future versions of Matter promise to integrate more complex devices such as robot vacuum cleaners, home sensors, and large appliances.
Matter Version 1.2, released in October 2023 expanded the standard to integrate more complex devices such as robot vacuum cleaners, smart home environmental sensors, and large appliances such as laundry washers, dishwashers, and refrigerators.
What is the Difference between Matter and Thread? View Answer
- Matter is how the devices communicate between the smart home ecosystems
- Thread is how the devices are connected across the network
Matter operates at the application layer of the OSI Model. It gives a level of abstraction for Smart Home developers, such that they can write their code once for Matter and know that it will function with Apple, Amazon, and Google devices. Thread operates on the lower 6 layers of the OSI Model (presentation through physical layers).
Thread is a low-power wireless protocol running on the IEEE 802.15.4 specification that allows many different devices to form a self-healing mesh network with a range of a few hundred meters and an upper limit of 250 devices. Thread is based on existing wireless standards and is an open standard.
While Matter can use Thread, it is not a requirement. Matter can use IPv6 technologies including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth LE, or Ethernet.
 Thread's operating layers of the OSI Model. (Image source: DigiKey – What is Thread? )
Thread's operating layers of the OSI Model. (Image source: DigiKey – What is Thread? )
Matter Boards
Thread Boards
![]()

u-blox 的 R41Z 模块是一种高度集成的超低功耗模块,可提供 IEEE 802.15.4 Thread 和低功耗蓝牙 (BLE) 射频连接,实现便携式极低功耗的嵌入式系统。
![]()
![]()
Nordic Semiconductor 的 Nordic Thingy:53 利用集成的运动、声音、光线和环境传感器来帮助构建概念验证和原型开发。

What is Thread? Low-power IoT Networking for Smart Home Devices
Thread is a wireless networking protocol designed for smart home and IoT devices. It is built using the IEEE 802.15.4 wireless standard.
Silicon Labs Webinar: Matter: Evaluation to Certification
The Matter 1.0 specification was released in October of 2022 and the momentum and buzz around it is unprecedented in the IoT industry.

What is Matter? Unifying IoT Devices for the Smart Home
In this video, we provide an overview of Matter, why it will help with IoT and smart home connectivity, and the basic data model. Additionally, we give a demonstration of how a smart light bulb might work using Thread and Matter.
Cellular / Mobile
DigiKey partners with top tier wireless providers on cellular services and has a wide portfolio of products and services to support wireless cellular solutions. Consider using cellular as a wireless solution for projects that:
- Have large coverage areas
- Need Location services or exact positioning data
- Require Secure transmissions of data
Performance Levels
High data rate – Cat-6, Cat-9, Cat-12: Found in high power, high data rate devices, Consumer mobile devices, base stations, and range extenders
Low data rate – Cat M1, NB-IoT, LTE-M: These operating categories are typically found in low power IoT or mobile devices such as smart meters, sensor nodes, and distributed machine communication
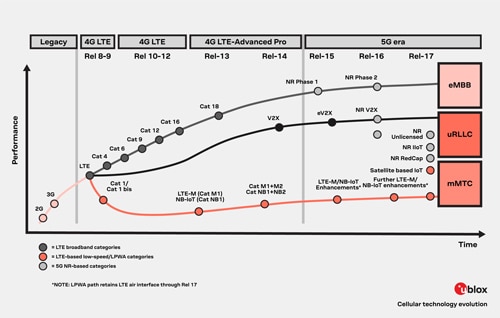 Source: u-blox
Source: u-blox
Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) Cards and Data Plans
Pre-paid and monthly plans available for cellular data:
Antennas
Choose from stock antennas or build your own custom antenna with the Antenna Builder service from Taoglas:
Transceivers, Gateways, and Routers
These devices negotiate the transfer of data and determine how data will be transferred on the network:

How to Enable Power Saving Modes of NB-IoT and Cat-M and the Energy Consumption Expected
Learn how to evaluate and use the power saving modes associated with NB-IoT and Cat-M cellular low power wide area network (LPWAN) technologies.
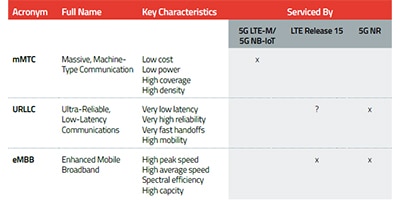
5G - The Basics
5G is being released in a series of 4 waves. Wave 1 started in 2018 and is the release of Fixed Wireless Access. Wave 2 has slowly started in 2019 and will allow for consumer cellular devices to be connected to 5G.

LTE-M vs NB-IoT
Which is the better low power LTE option, LTE-M or NB-IoT? The best answer is, it depends. LTE CAT-M1 supports higher data rates, and over-the-air updates. LTE CAT-M1 can be mobile, and is largely available.
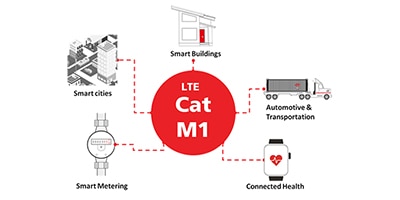
LTE Cat M1 Modules Provide an Alternative to Broadband and Smartphones for Assisted Living Systems
LTE Cat M1 cellular modules provide a link for connected healthcare solutions in the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT).
Use a Cellular Module to Connect a Maker Project to the IoT
Pairing a single board computer with a cellular modem eliminates smartphone or router gateways and dramatically extends the wireless range of maker projects.
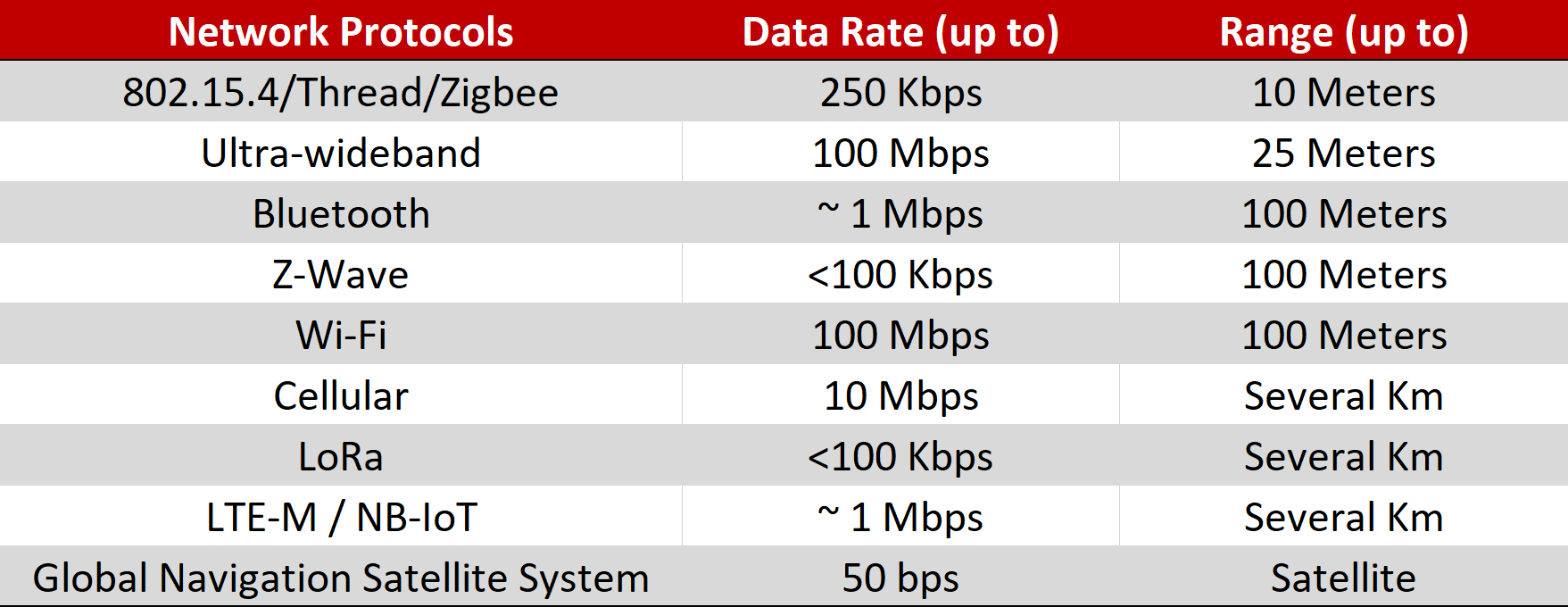
Network Protocols
Wireless Personal Area Networking (WPAN)
- Bluetooth when not designated as Bluetooth Low Energy (or BLE) is often referring to an earlier version (which is sometimes called Bluetooth Classic). It is a short-range wireless standard for transmitting data over short distances.
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is optimized for low power usage and most often found in devices with small batteries and low power requirements like fitness trackers and medical devices.
- Impulse radio ultra-wideband (IR-UWB) is a wireless technology that uses high frequency, wide bandwidth transmissions. While the technology operates in the 3.1 GHz - 10.1 GHz frequency range, each radio channel can have a bandwidth of 500MHz. The transmissions are short duration and act as a position and ranging sensor using radar principles.
- Zigbee is a 2.4 GHz mesh network based on the IEEE 802.15.4 specification that forms small scale Personal Area Networks. Not as complex or expensive as other options like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi but often covers a smaller area. Typically found in low power and low data rate devices like home automation, IoT devices and even some industrial automation networks.
- Z-wave is another wireless protocol for home automation and smart devices, Z-wave is a sub 1 GHz mesh networking protocol used in home automation devices with low data rate transmission and power requirements. Z-wave is owned and developed by Silicon Labs.
- 6LoWPAN an Acronym for "IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks" 6LoWPAN is a wireless network protocol that supports using Internet Protocol (IP) version 6 over wireless networks for improved networking performance and features. While more complex than other options, it does allow for open IP standards for communication.
- Thread is based on 6LoWPAN and 802.15.4. It can be used as a low-power mesh networking protocol for Internet of things (IoT) products. Often used with Matter.
Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN)
- Wi-Fi is one of the most popular and widespread wireless protocols, Wi-Fi is expanding capabilities and frequency ranges for IoT devices, low power applications and short-range high data rate devices, making it a very popular protocol to integrate into smart devices.
Cellular
- High Data Rate Cellular, more commonly known as 4G, Perfect for high speed, high data rate wireless transmissions, higher power requirements for transmitting but there are several low power variants designed for IoT and Machine to Machine applications.
- 5G RedCap (short for Reduced Capacity) is a 5G based wireless standard designed to serve the midpoint between high speed, high data networking and low power lower data rate IoT applications. There are several differences 5G RedCap has compared to the full 5G hardware standard such as narrow bandwidths, reduced antenna count and lower transmitter power. The benefits are lower power consumption and decreased hardware requirements making it suitable for wearable devices, IoT and smart cities.
Low-Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN)
- LoRa – (from "Long Range") is a proprietary spread spectrum modulation scheme that is developed by SemTech. It is long range (~3 miles / 5 kilometers) and low data rate (~1kbps). It trades data rate for sensitivity within a fixed channel bandwidth. It implements a variable data rate, which allows the system designer to trade data rate for range or power.
- NB-IoT – (also known as Cat-NB1) is a narrowband technology standard that does not use a traditional cellular LTE physical layer but is designed to coexist with other LTE devices and use some of the same frequency bands. It is suitable for static, low-power applications requiring low data throughput, and long-range.
- LTE-M – (also known as Cat-M1) is designed for low-power cellular applications requiring medium data rate throughput. It has a narrower bandwidth compared to regular LTE, giving a longer range, but less data throughput. LTE-M is perfect for medium-throughput applications requiring low power, low latency, and mobility.
- Wi-Fi HaLow™ – Wi-Fi certified products based on the IEEE 802.11ah wireless standard which operates on the sub 1 GHz band. This allows for longer ranges and lower power consumption compared to traditional Wi-Fi. While still having all the same features of Wi-Fi networking such as security and ease of deployment, the long range allowed by the sub 1 GHz transmissions make perfect for modern IoT and other long-range applications.
- Dect NR+ – is a license exempted, non-cellular mesh networking wireless standard designed for massive Machine to Machine communications requiring ultra-low latency and data throughput. By operating on the global license exempted 1.9 GHz frequency band, there is no need for existing cellular infrastructure such as base stations and towers, allowing users to run their own private network without cellular providers, allowing for significantly reduced cost of deployment.
Interference
If you have ever heard static on the radio, wireless headphones suddenly sounding glitchy or the loss of data packets from a wireless sensor, then you have experienced interference.
Interference may prevent reception altogether until the interference is removed, may cause only a temporary loss of a signal, or may affect the quality or amount of data sent across the wireless channel.
Certification and Testing
The fair and responsible use of the wireless electromagnetic spectrum is a priority for both safety and economic use, national governments require strict compliance and certification needed before new designed are offered for sale to the public. In the United States of America, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is responsible for testing and certification that devices meet Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards or the ability of a product to function in and around other electronic components without causing interference.
Dealing with interference
There are a many different methods that can eliminate or reduce the interference from outside sources.
Shielding: RF shields and RF gaskets can ensure that the enclosures are fully protected against RFI and EMI intrusion
 RF Shields – One of the most common ways to reduce incoming interference or prevent radio emissions from leaking out is RF Shielding. The purpose of an RF shield is to either block or conduct away interference signals from the components on that are the most susceptible to interference such as RF amplifiers.
RF Shields – One of the most common ways to reduce incoming interference or prevent radio emissions from leaking out is RF Shielding. The purpose of an RF shield is to either block or conduct away interference signals from the components on that are the most susceptible to interference such as RF amplifiers.
 RFI and EMI – Contacts, Fingerstock and Gaskets – Includes foam gaskets that can seal gaps in external enclosures.
RFI and EMI – Contacts, Fingerstock and Gaskets – Includes foam gaskets that can seal gaps in external enclosures.
 RFI and EMI – Shielding and Absorbing Materials – Includes sheets or rolls of material to reflect or absorb interfering signals.
RFI and EMI – Shielding and Absorbing Materials – Includes sheets or rolls of material to reflect or absorb interfering signals.
Directional antennas to carefully direct and limit EMI from spreading in unwanted directions
 Directional Antennas – Directional antennas are another option to reduce interference from outside sources. By only allowing reception from a particular direction, they can filter out unwanted sources along the transmission path. However, these are large devices that more suitable for fixed installations with a predictable reception path.
Directional Antennas – Directional antennas are another option to reduce interference from outside sources. By only allowing reception from a particular direction, they can filter out unwanted sources along the transmission path. However, these are large devices that more suitable for fixed installations with a predictable reception path.
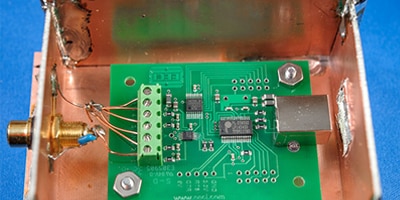
Use the Right Off-the-Shelf Metal Cans and Clips to Shield Against EMI/RFI
Use prefabricated metal cans with complementary production-compatible pc board mounting clips for convenient, effective, and removable RF shielding.
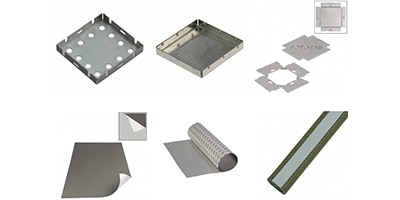
RF Shielding: The Art and Science of Eliminating Interference
Explore products and approaches that use shielding and ground planes to prevent spurious signal interference and ultimately minimize RF interference.

Design and Shielding Techniques to Block EMR and EMI
The ever-improving functionality of modern smartphones, pods, tablets, and PCs is a testament to the designer's ability to do more in less space. However, as silicon geometries get smaller, sensitivity to noise can get higher.
Tackling Interference in High Reliability Wireless Industrial Control Systems
Options to overcome interference in high reliability industrial control systems using different frequencies and protocols in transceiver devices and modules.

RFI and EMI - Contacts, Fingerstock and Gaskets
This Product Selection Guide contains information to help select products in the RFI and EMI - Contacts, Fingerstock and Gaskets category on DigiKey.com
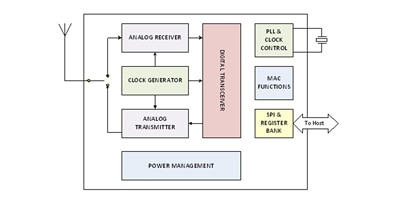
Wireless Transceivers
Transceivers are a combination of both wireless transmitter and receiver circuits in one package or device. Examples of products that use transceivers include Cell phones, two-way radios like walkie talkies, HAM Radios, and IoT connected devices.
Form Factors of Transceivers
 Integrated Circuits (ICs) – contain the necessary circuity to form and decode wireless signals. However, as they are just the IC, they require circuit board design and assembly before they can transmit. Not ideal for the first-time maker but allows for close system integration
Integrated Circuits (ICs) – contain the necessary circuity to form and decode wireless signals. However, as they are just the IC, they require circuit board design and assembly before they can transmit. Not ideal for the first-time maker but allows for close system integration
 Modules and Modems – packages that can be integrated into a wireless design. Some modules have integrated RF shielding and power management features, which can reduce the amount of additional design needed
Modules and Modems – packages that can be integrated into a wireless design. Some modules have integrated RF shielding and power management features, which can reduce the amount of additional design needed
 Finished Transceiver Unit – ready to use devices and units to quickly set up a wireless network. Ready to be powered on and connected to a network, these finished units take the guess work out of wireless network deployment and are ideal for plug and play operations when connecting sensors or setting up data links
Finished Transceiver Unit – ready to use devices and units to quickly set up a wireless network. Ready to be powered on and connected to a network, these finished units take the guess work out of wireless network deployment and are ideal for plug and play operations when connecting sensors or setting up data links
 Development boards and kits – for experimentation and prototyping, they are a maker's best friend to get started in the world of RF development. With the world's most popular manufactures and suppliers in stock at DigiKey, covering every frequency, wireless band, and application DigiKey has everything you need to experiment and move your ideas from prototype to production
Development boards and kits – for experimentation and prototyping, they are a maker's best friend to get started in the world of RF development. With the world's most popular manufactures and suppliers in stock at DigiKey, covering every frequency, wireless band, and application DigiKey has everything you need to experiment and move your ideas from prototype to production
RF Transmitters – Product Selection Guide
This Product Selection Guide contains information to help select products in the RF Transmitters category on DigiKey.com
Ultrasonic Receivers, Transmitters – Product Selection Guide
This Product Selection Guide contains information to help select products in the Ultrasonic Receivers, Transmitters category on DigiKey.com
Antennas
An antenna is a device for transmitting and receiving radio signals and are the interface between radio waves in free space and electrical currents moving through wires or traces in a device. Antennas are typically tuned to a certain frequency of operation, but some are designed to operate across a wide bandwidth (a wide frequency range) or at various frequencies, it should not be assumed that antennas that operate at various frequencies will be effective at all frequencies in between.
Antenna Integration
Integrating an antenna into your design can be an extremely difficult task and will vary across many factors of your design. We can't cover every factor, but the list below will get you started. In general, more metal (bigger antenna) means better antenna performance if it's matched properly in your design.
External Antenna
If you are designing using an external antenna, some considerations will be different from those using an embedded or internal antenna. You may need a longer cable to reach a premium transmission point. Introducing cables and connectors introduces losses into the signal chain and should be planned for so these losses won't considerably affect the performance of your design. External Antennas may have a higher gain also and that should be considered as well as it may put your design outside of the acceptable certification parameters. Location, placement and orientation of the antenna and cable type used will be key factors in the performance of an external antenna.
Internal Antenna
Internal or embedded antennas are often chosen due to size limitations, this often means the performance of the antenna is not as great as their external counterparts and the design is critical to getting the most out of the embedded antenna. Size and placement should be the first considerations for an internal antenna as these will determine which antennas may be used. If your device will be inside a metal box, an internal antenna likely won't work at all. If the antenna will be placed on a PCB you will need to determine what amount of ground or component clearance will be needed for the antenna chosen, some antennas may be designed to sit on top of a ground plane, and some will require a certain amount of ground clearance to operate effectively.
Antenna Terminology
- Gain – measures how effectively the antenna transmits power in a specific direction. This gets referred to as peak gain, average gain or both on antenna datasheets.
- Antenna Efficiency – ratio of the power radiated versus the power fed to the antenna terminal. Higher efficiencies indicate better performing antenna at a given frequency.
- Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) – Measures how effectively power is transmitted from the source through a transmission into the antenna (load). VSWR is measured as a ratio of input power to output power, a measure of less than 2:1 is considered a good match, the higher the VSWR the greater the mismatch.
- Antenna Impedance – Measures the opposition of current when a voltage is implied. This is the value that must be matched to the source impedance to transmit power efficiently through the antenna. Most radio equipment is built for an impedance of 50 ohms.
Popular Antenna Types
 Ceramic Patch – Support wider frequency bands, often used with GPS
Ceramic Patch – Support wider frequency bands, often used with GPS
 Chip – Small footprint, soldered directly to PCB
Chip – Small footprint, soldered directly to PCB
 Whip – A traditional antenna design that has been used for FM Radio, but can be applied broadly
Whip – A traditional antenna design that has been used for FM Radio, but can be applied broadly
 Flat Patch – Commonly used in portable wireless devices
Flat Patch – Commonly used in portable wireless devices
Micro Strip Calculator
The IPC-2141 Trace Impedance Calculator will help make initial design easier by allowing the user to input basic parameters and get a calculated impedance according to the IPC-2141 standard. While this calculator will provide a baseline, any final design considerations should be made towards loss, dispersion, copper roughness, phase shift, etc. A field solver may be required for final circuit analysis.
dBm To Milliwatt Converter
The dBm to milliwatt converter tool converts power measurements between units of decibel-milliwatts (dBmW) and watts (W).

Antenna Builder – Fit the Antenna to Your Project
What if you could have a custom antenna shipped to you in days, not weeks, without NRE costs, tooling charges or minimum order requirements? You can!

Return Loss vs. VSWR in chip antenna selection
Matching is important when selecting chip antenna. Return Loss and VSWR are both parameters used to measure the antenna’s matching condition. There is a numerical relationship between Return Loss and VSWR.
RF Antennas
This Product Selection Guide contains information to help select products in the RF and Wireless category on DigiKey.com RF Antennas are used to receive and transmit electromagnetic waves.



















 中国
中国