Piezoelectric Sensors: Detecting Vibrations
2023-12-20 | By Antonio Velasco
Something that you may have seen before is Piezo buzzers, a device that produces a sound that utilizes the piezoelectric effect. Similar to how there are sensors that will detect light or emit light on the same principle, there are piezoelectric sensors: a device that will detect vibrations, or most commonly, a sound! In today's blog, we'll go over the basics of piezoelectric sensors and how they work!
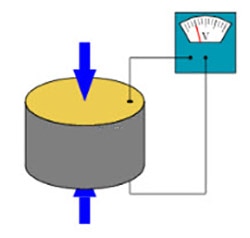
The Piezoelectric Effect essentially is a phenomenon that occurs when stress is applied to a material, and an electric charge accumulates as a result. Simply put, when said material is deformed, a voltage is produced. This can happen the other way around, where applying a voltage would deform the material as well.
The Inner Workings of the Sensor
Piezoelectric sensors typically take advantage of a certain type of crystal--essentially the heart of the sensor. Whether quartz or ceramic, they exhibit the same piezoelectric property of producing charge when stress is applied. This occurs as the vibrations (or stress) displaces charged ions within the crystal, and thus makes it sensitive to mechanical changes in its environment. This simple idea leads to a very simple piezoelectric sensor!
You'll typically see them used often in music, for electric drumkits to produce sound upon being hit or for acoustic kits to be enhanced on performance day. They're also very useful for your projects, for anything requiring the detection of vibrations (possibly sound) or movements (possibly any motion). Some projects that come to mind can be simple alarms for security measures or fitness trackers. You could also implement it into sports equipment such as golf clubs or tennis rackets--with the sensor measuring the force of each stroke. They're also great for detecting pressure, or more simply, touch, adding a layer of interactivity to any project.
Sensitivity and Resonance Frequency
With these sensors, it's essential to grasp two critical device properties: sensitivity and resonance frequency. Sensitivity refers to how effectively a piezoelectric sensor converts mechanical stress into an electrical signal. High-sensitivity sensors are ideal for detecting subtle vibrations or low-pressure changes, while lower-sensitivity sensors are suitable for applications requiring greater force or impact. In addition to that, every piezoelectric sensor has a resonance frequency at which it responds most efficiently. Operating a sensor near its resonance frequency enhances its sensitivity and accuracy. However, this frequency varies depending on the sensor's design and crystal material.

When picking out a piezoelectric sensor, it's important to consider all the aspects of your project and what you intend to use it for. Sensitivity and resonance frequency are the two main components of a piezoelectric sensor that will vary--in addition to form factor, of course.

They do tend to be small though!
Additionally, you may or may not need to include an amplifier or a signal conditioning circuit in order to convert the sensor's output into a compatible signal. Looking into whether your piezoelectric sensor will come with such compatibility is crucial.
All-in-all, these sensors are perfect for detecting motion and everything in between! There is a large number of projects to be done with these sensors--check out a couple of the products I listed below!