Introduction to Linear Voltage Regulators
2016-02-13 | By Dave Knight
Linear regulators are simple voltage regulator circuits commonly used in electronics. This paper briefly discusses how linear regulators work, their advantages and disadvantages, variations on the linear regulator, and important datasheet parameters.
How Linear regulators work
Linear regulators uses a closed feedback loop to bias a pass element to maintain a constant voltage across its output terminals. In figure 1, the op-amp drives the base of Q1 to ensure that the voltage at its inverting input will be equal to the voltage reference at its non-inverting input.
The op-amp in this circuit has a small load, the base current, and minimal capacitive loading. Consequently, it can respond to changes in load very quickly.
Two things can be observed from this schematic:
- Linear regulators are step-down converters, meaning that the output voltage will always be less than the input voltage. In fact, there is a minimum voltage difference between VIN and VOUT that will allow the linear regulator to work. In datasheets, this value is called the drop-out voltage. If the VOUT > VIN - VDROPOUT, then the linear regulator can’t regulate the output voltage at the desired voltage.
- Power is dissipated in the pass transistor. The amount of power is P=(VIN-VOUT)*ILOAD. This power is wasted heat. This heat causes the regulator to get warm.
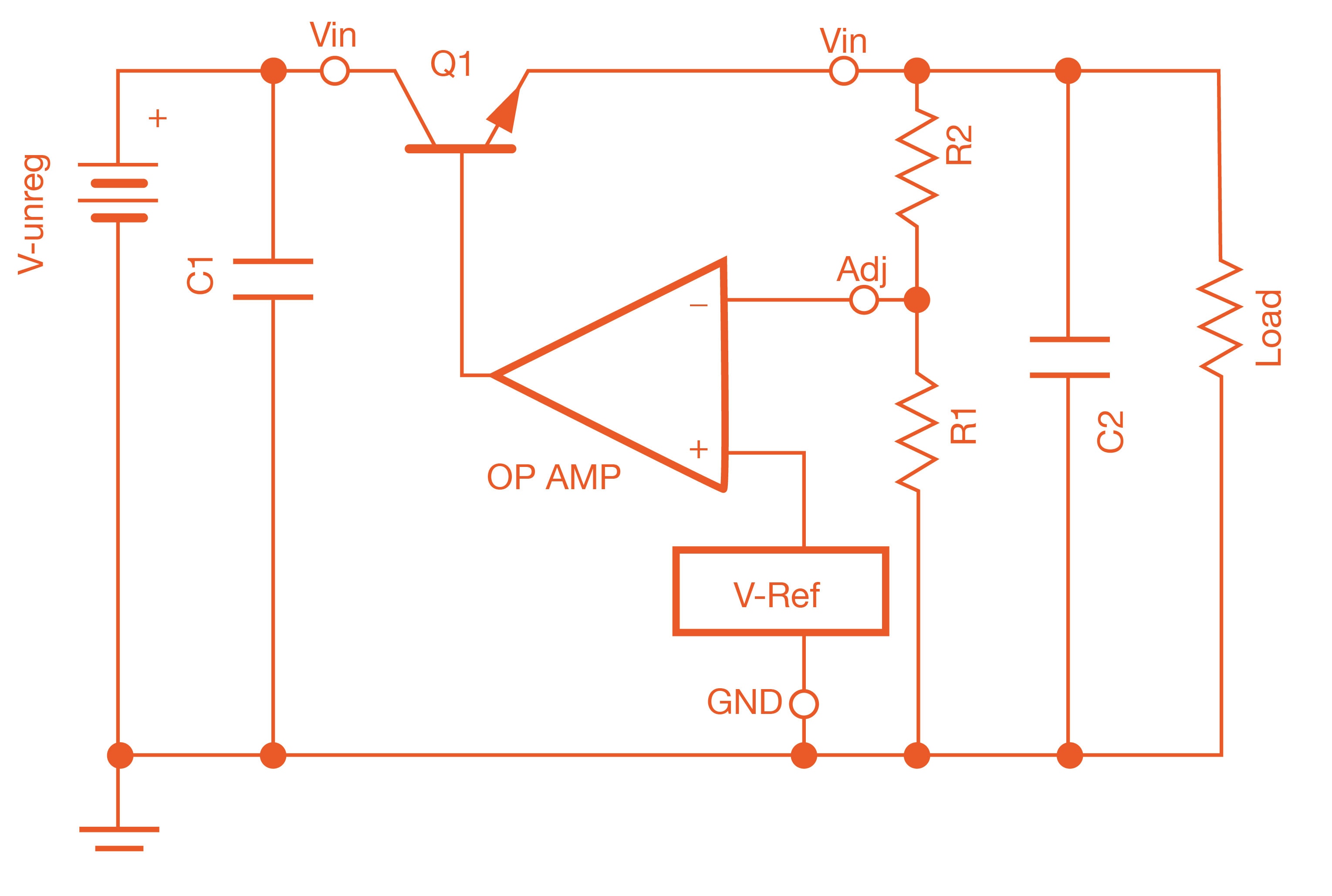
Figure 1: Example of internal operation of a linear regulator
Image Source: http://www.eetimes.com/document.asp?doc_id=1272466
Advantages of linear regulators
Linear regulators are typically highly integrated, including the pass element and the feedback loop. Some linear regulators, like the LM317, are adjustable when used with an external resistor divider.
Disadvantages of linear regulators
Linear regulators have the following advantages:
- Simple.
- Cheap.
- Power supply rejection ratio. Linear regulators respond quickly to changes in input voltage, producing an output voltage that is mostly free of any ripple on the input.
- Respond quickly to changes in load voltage.
- No switching noise. Other voltage conversion circuits, known as DC-DC converters, have high-frequency switching noise. Linear regulators don’t have this characteristic.
The main disadvantage of linear regulators is that they are inefficient. This is because of the voltage drop across the pass element. This inefficiency can cause the linear regulator to be hot. Pay attention to the expected heat dissipation for your application, and be sure to use adequate heatsinking or a copper fill to manage the temperature rise. If high power, efficiency, or a step-up converter is desired, use a DC-DC converter.
Variations on the linear regulator
Linear regulators come in many varieties. Some linear regulators have fixed outputs. Some have outputs programmable by resistor divider. Some regulate negative voltages. Low-dropout regulators, known as LDOs, have a small dropout voltage. Some linear regulators include battery charging smarts. Some are complex, programmable chips used in automated test equipment. It is common to linear regulators to have over-temperature shutdown.
Important datasheet parameters
Maximum input voltage: This is the maximum voltage that can be applied at the input terminal without damaging or destroying the part.
Input voltage-output voltage differential: Some adjustable linear regulators have a maximum input-output voltage differential rating.
Current rating: The maximum current the linear regulator can source. This is dependent on other factors such as input-output voltage differential, ambient temperature, and heatsinking. The power rating of the package indicates how much power the package can dissipate; this may be dependent on heatsinking and layout requirements.
Drop-out voltage: This is the minimum input-output voltage differential the device can accept and produce the regulated voltage.
Conclusion
This paper has given a brief overview of how linear regulators work, advantages, disadvantages, variations on the linear regulator, and important datasheet parameters.

Have questions or comments? Continue the conversation on TechForum, DigiKey's online community and technical resource.
Visit TechForum







 中国
中国