Selecting and Applying AC/DC Power Supplies for Factory Automation
投稿人:DigiKey 北美编辑
2024-12-16
The shift to factory automation is accelerating with the application of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Factory 4.0 technologies. Robust power supplies are the foundational infrastructure for these technologies. This makes it critical that designers be able to quickly deploy reliable power supplies that support a variety of voltage levels to meet the needs of the manufacturing facilities’ automation, networking, and test and measurement equipment.
To address this need, designers can either construct the power supplies themselves, which can be costly and time-consuming, or find readily available solutions fit for the task and within their budgetary constraints. Either solution must adhere to electromagnetic compliance (EMC) and safety standards while meeting electromagnetic interference (EMI) regulations. In addition, factory automation power supplies must have protection features to make them suitable for industrial environments.
This article briefly discusses the requirements of an AC/DC power supply for factory automation applications and outlines the critical performance and form-factor selection criteria. It then introduces DIN rail power supplies from RECOM Power as examples of ready-to-deploy units.
Power supplies for factory automation
Factory automation also includes networking equipment and test and measurement tools, and relies heavily on robust and reliable power. Power supply requirements vary depending on the application and the equipment. A typical solution converts a mains AC voltage (90 VAC to 264 VAC), with slight variations between countries) to a DC voltage. The output requirements vary as factory automation equipment runs on several standard DC voltages, including 12 V, 15 V, 24 V, and 48 V.
Apart from certified compliance with the relevant safety and other regulations, modular solutions are typically designed with energy density and efficiency in mind. They satisfy a range of standard voltages and current requirements and are manufactured for high reliability and longevity.
Commercial modular power supplies for factory automation include options to suit the popular DIN rail system for ease of deployment. This system works with universal standard widths and mounting hardware shapes. With the DIN rail system, installers are guaranteed dimensional consistency across a suite of products, including power supplies, regardless of the manufacturer.
This cross-brand compatibility gives users of DIN rail systems the flexibility to mix and match components (Figure 1).
 Figure 1: DIN rails simplify power supply deployment and allow mixing and matching of components. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Figure 1: DIN rails simplify power supply deployment and allow mixing and matching of components. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Cost-effective DIN rail power supplies
Factory automation infrastructures use multiple power supplies, causing costs to increase rapidly. The RECOM Power REDIIN120 series of 120 W DIN rail AC/DC power supplies (Figure 2) is designed to minimize cost while remaining compact and reliable. Each unit measures 123.6 x 30.0 x 116.8 millimeters (mm).
 Figure 2: The REDIIN120 series of 120 W DIN rail power supplies measures 123.6 x 30.0 x 116.8 millimeters (mm). (Image source: RECOM Power)
Figure 2: The REDIIN120 series of 120 W DIN rail power supplies measures 123.6 x 30.0 x 116.8 millimeters (mm). (Image source: RECOM Power)
The convection-cooled REDIIN120 AC/DC power supplies can operate at full power across a temperature range of -30°C to +50°C. These products are certified according to the safety standards IEC 62368-1, IEC 61010-1, and IEC 61010-2-201.
The electromagnetic radiated and conducted emissions from the power supplies comply with the EN 61000-6-2 immunity standard and the heavy industrial EN 61000-6-4 Class B emission standard. The units also comply with environmental protection requirements per the RoHS directive.
The REDIIN120 series comprises three models, each operating from a 90 VAC to 264 VAC input and differing only in output voltage. The REDIIN120-12 has a nominal 12 V output that is adjustable from 10.8 V to 13.2 V. The REDIIN120-24 has a nominal 24 V output that is adjustable from 21.6 V to 26.4 V. The REDIIN120-48 has an output of 48 V that is adjustable from 43.2 V to 52.8 V. The maximum output currents are 10 A, 5 A, and 2.5 A, respectively.
The power supplies operate with a maximum efficiency between 86% and 89.5%, depending on the unit (Figure 3), and have a no-load power consumption of 150 milliwatts (mW) for the 12 V and 24 V versions, and 210 mW for the 48 V version.
 Figure 3: Shown is the efficiency versus output load for the REDIIN120-24 power supply. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Figure 3: Shown is the efficiency versus output load for the REDIIN120-24 power supply. (Image source: RECOM Power)
The power supplies can operate in constant-current mode, making the series suitable for inductive and capacitive loads such as motors, solenoids, and relays. The maximum capacitive load at start-up is 8 millifarads (mF) for the 12 V and 24 V units, and 3 mF for the 48 V unit.
The REDIIN120 power supplies feature comprehensive overcurrent protection (OCP), overvoltage protection (OVP), and over-temperature protection (OTP) (Figure 4). Voltages exceeding 17.4 VDC for the 12 V unit, 33.6 VDC for the 24 V unit, and 64.8 VDC for the 48 V unit, generate a latch-off condition.
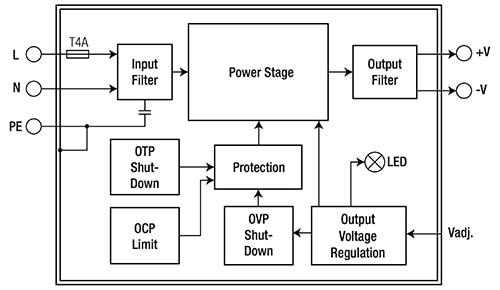 Figure 4: The REDIIN120 series has comprehensive protection. Voltages exceeding 17.4 VDC for the 12 V unit, 33.6 VDC for the 24 V unit, and 64.8 VDC for the 48 V unit, generate a latch-off condition. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Figure 4: The REDIIN120 series has comprehensive protection. Voltages exceeding 17.4 VDC for the 12 V unit, 33.6 VDC for the 24 V unit, and 64.8 VDC for the 48 V unit, generate a latch-off condition. (Image source: RECOM Power)
There is no 15 V variant in the REDIIN family. However, RECOM Power does offer the RACM15E-15SK/PMAD-CTN AC/DC converter for 15 V operation (Figure 5). This DIN rail-mounted unit provides a 15 V, 1 A output from either an AC input of 80 V to 275 V or a DC input of 370 V. The maximum output power is 15 W, and its efficiency at full load is 85%. The units have international safety and EMI certifications to medical, household, industrial, and safety transformer standards.
 Figure 5: The RACM15E-15SK/PMAD-CTN is a 15 V, 15 W DIN rail-mounted AC/DC converter for factory automation. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Figure 5: The RACM15E-15SK/PMAD-CTN is a 15 V, 15 W DIN rail-mounted AC/DC converter for factory automation. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Design considerations for DIN rail power supplies
In addition to the safety, EMC, and EMI requirements, designers need to consider other critical parameters to ensure that the factory AC/DC power supplies can operate without failure over long periods.
For example, limiting the operating temperature to below the maximum rating for the power supply is essential to avoid problems. High operating temperatures can cause performance to be derated while also reducing operating life and increasing the risk of incorrect operation and failures. Low temperatures can also cause performance problems, including increased output voltage ripple and poor output regulation. Moreover, changes in electrical characteristics at low temperatures may result in failure to start.
Manufacturers typically recommend derating the power supply above a temperature threshold, and units in the REDIIN120 series also include a safety cut-off above a maximum operating temperature. The derating curve for the REDIIN120-24 120 W AC/DC power supply (Figure 6) indicates a reduction in power output above +40°C for 100 VAC and 115 VAC inputs, and above +50°C for an input of 230 VAC. Operation above +70°C triggers a cut-out.
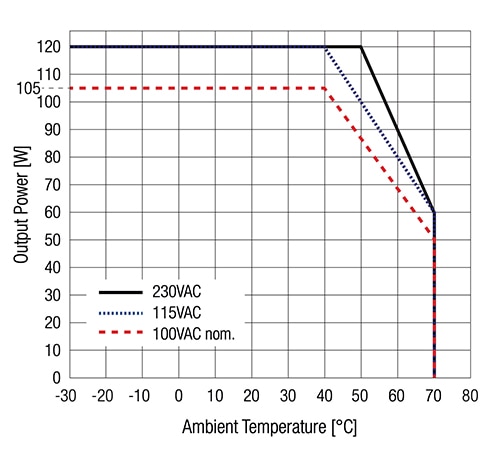 Figure 6: The derating curve for the REDIIN120-24 120 W AC/DC power supply indicates a reduction in power output above +40°C for +100 VAC and 115 VAC inputs, and above +50°C for an input of 230 VAC. Operation above +70°C triggers a cut-out. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Figure 6: The derating curve for the REDIIN120-24 120 W AC/DC power supply indicates a reduction in power output above +40°C for +100 VAC and 115 VAC inputs, and above +50°C for an input of 230 VAC. Operation above +70°C triggers a cut-out. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Another consideration is cable length. Excessively long power cables can incur resistive losses that result in reduced voltage at the load below allowable limits. Increasing the wire gauge or the output voltage and using local DC/DC regulation at the point of load (PoL) can overcome cable losses.
The type of load must also be considered. Supplying power to capacitive or inductive loads can be challenging. Inductive loads such as motors, solenoids, and relays can cause high voltage spikes. Supplying capacitive loads can reduce the dynamic load response of the power supply or lead to instability and increased output ripple. Designers should carefully consider the types of loads the application demands when selecting the power supply to ensure it can cope. The REDIIN120 units, for example, offer a constant-current mode, making the series suitable for inductive and capacitive loads.
Finally, output OCP is important to minimize the effects of missed cycles and drop-outs. Typical techniques to protect the power supply include limiting the current to a set value, ‘folding back’ the current to a safe value with increasing load, or ‘hiccup’ protection, whereby the output is turned off and back on again after a delay. If the overcurrent condition still exists, the hiccup cycle is repeated. The REDIIN120 products feature hiccup protection.
For example, the REDIIN120-24 120 W AC/DC power supply operates in a constant-voltage mode within its rated load range (Figure 7). For output OCP, when exceeding the maximum current rating by 105% to 150% of its nominal value, the unit enters a limited-current mode, which drives the output voltage to approximately 80% of the nominal set point. Increased load causes the power supply to enter a hiccup mode with automated restart.
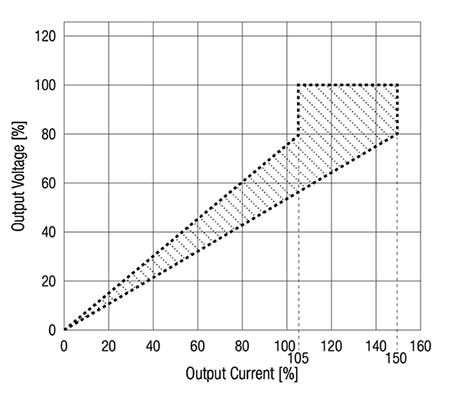 Figure 7: The REDIIN120-24 120 W AC/DC power supply operates in a constant-voltage mode within its rated load range. For output OCP, when exceeding the maximum current rating by 105% to 150% of its nominal value, the unit enters a limited-current mode, which drives the output voltage to approximately 80% of the nominal set point. Increased load causes the power supply to enter a hiccup mode with automated restart. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Figure 7: The REDIIN120-24 120 W AC/DC power supply operates in a constant-voltage mode within its rated load range. For output OCP, when exceeding the maximum current rating by 105% to 150% of its nominal value, the unit enters a limited-current mode, which drives the output voltage to approximately 80% of the nominal set point. Increased load causes the power supply to enter a hiccup mode with automated restart. (Image source: RECOM Power)
Conclusion
Commercial DIN rail-mounted modular power supplies from RECOM offer cost-effective, compact, reliable, and easy-to-deploy solutions for factory automation. The units are pre-certified to the mandatory regulations and are supplied with a range of standard DC voltage and current outputs. The supplies offer a range of safety features, and options are available to power capacitive and inductive loads.

免责声明:各个作者和/或论坛参与者在本网站发表的观点、看法和意见不代表 DigiKey 的观点、看法和意见,也不代表 DigiKey 官方政策。







 中国
中国