Nano Modules Redefine Low-Power DC/DC Conversion
投稿人:电子产品
2015-06-30
Whether it is for telecom infrastructure or industrial robots, more features and functions are being added to system boards, reducing the amount of space available for power supplies. Take, for instance, distributed power architecture in computers, where point-of-load (POL) regulators and DC/DC converters are required to be as tiny as possible. In addition, these DC/DC converter modules must use a minimum number of external components and offer high efficiency with fast transient response. Less than 50 mm2 in size, these tiny power supplies also must exhibit superior electromagnetic interference (EMI) performance. In other words, despite high-switching frequency, the integrated inductor used must be well shielded to keep RF emission to a minimum so that they meet required regulatory compliance. Now add to the mix the engineer’s preference for scalability because it makes it easy to upgrade the module without altering the printed circuit board. Taken together, it’s a daunting list of requirements.
Keeping these new demands of modern power products in mind, Texas Instruments has expanded its popular Simple Switcher DC/DC converter family with four new members called Nano Modules. Designed for space constrained POL applications, including DC/DC converters up to 17 V, the four Nano Modules allow designers to add new features, maintain high efficiency, address radiated EMI requirements, and fit into smaller form factors while keeping the design process simple and system costs low. In essence, Nano Modules maximize power density and thermal performance while maintaining simplicity and low cost.
Nano Power Modules
There are two versions: the 5 V parts, which include LMZ20501 and LMZ20502 deliver up to 2 A output current at an adjustable output voltage of 0.8 V to 3.6 V, while the higher 17 V version LMZ21700/01 is rated up to 1 A of output current at 0.9 V to 6.0 V output voltage. Offering sizes as small as 30 mm2, the Nano Modules are 40 percent smaller than a discrete implementation and feature low EMI to comply with the CISPR (class B) radiated and conducted EMI standard. The 17 V, 1 A part LMZ21701, for example, comes in a miniature package measuring 3.5 x 3.5 x 1.75 mm, and incorporates the controller/logic, power MOSFETs, and the high-frequency inductor, along with other pulse-width modulated (PWM) functions in this tiny package (Figure 1). As a result, it offers a complete step-down DC/DC converter solution capable of driving up to 1 A load in space-constrained applications like network security cameras, factory automation, and industrial robots.
Although the input voltage range for LMZ21701 is 3 to 17 V, it is primarily intended for 5 V or 12 V input applications. Because the Nano Module is highly integrated, only an input capacitor, an output capacitor, a soft-start capacitor, and two resistors are required externally for basic step-down DC/DC conversion, as shown in Figure 2. As a quick start, the product data sheet provides external component values for output voltages from 1.2 V to 5.0 V.
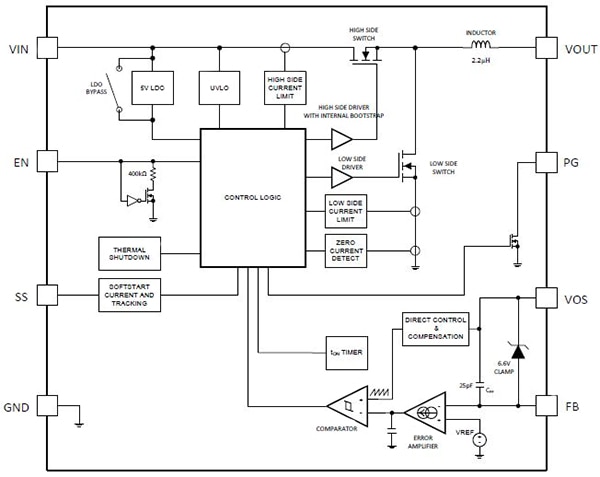
Figure 1: The 17 V Nano Module LMZ21701 incorporates controller/logic, power MOSFETs, and an inductor in a miniature package.

Figure 2: The LMZ21701 requires only an input capacitor, an output capacitor, a soft-start capacitor, and two resistors for a basic step-down DC/DC conversion solution.
As an example, Table 1 gives component values for a VOUT of 1.2 V using LMZ21701. Similar tables for other output voltage rails are provided in the product data sheet. Besides giving precise values, the data sheet also recommends ceramic capacitor types with sizes and tolerances for resistors.

Table 1: External component values for output voltage VOUT of 1.2 V using Nano Module LMZ21701.
According to TI’s product line marketing engineer Stephen Ott, the high-density, high-performance Nano Modules are made possible by combining high-frequency switching techniques with advances in magnetics. In order to achieve a small solution size, the LMZ21701 Nano Module comes in an innovative MicroSiP package with a DFN footprint. The construction consists of a synchronous buck converter IC embedded inside an FR-4 laminate substrate, with a power inductor mounted on top of the substrate material (Figure 3). Similar techniques are also adopted for other members of the Nano Modules family.

Figure 3: The package cross-section shows that the Nano Module’s discrete inductor is mounted on top of the substrate material while the synchronous buck IC is embedded inside the FR-4 laminate substrate.
Stephen Ott explains that the LMZ21701 architecture is based on direct control with seamless transition into power-save mode or DCS-Control. This architecture combines the fast transient response and stability of hysteretic-type converters along with the accurate DC output regulation of voltage-mode and current-mode regulators, he says. The efficiency is also high across load variations, as illustrated in Figure 4. By comparison, for the same input of 12 V, the full-load efficiency at 1.2 V output is slightly lower than at 3.3 V output. Likewise, at low-load, the efficiency drops faster at 1.2 V output as compared to 3.3 V. Nevertheless, the peak efficiency at 3.3 V output is about 90 percent as compared to 80 percent at 1.2 V output. Similarly, at low-load, the efficiency for 3.3 V output is 72 percent as compared to 50 percent for 1.2 V output.
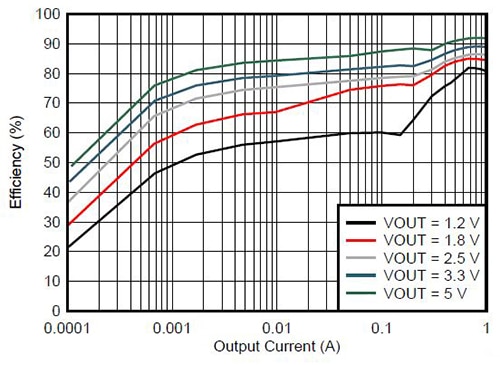
Figure 4: Efficiency plot for Nano Module LMZ21701 with input voltage VIN = 12 V and output voltage VOUT ranging from 1.2 V to 5.0 V.
Reference design
To demonstrate that the Nano Module LMZ21701 is suitable for a wide-input, multiple-output high-density DC/DC solution, TI has created a reference design using Simple Switcher converter LM46002 and Nano Module LMZ21701. It is labeled PMP10618. The four output diagram is shown in Figure 5. In this design, the LM46002 provides a regulated 12 V rail from an input of 15 to 60 V. This 12 V rail is then regulated to 5 V, 3.3 V, and 1.8 V rails using three LMZ21701 modules. Each rail can furnish up to 1 A of load current. The reference design provides a complete schematic with bill of materials (BOM). A similar reference design for LMZ20502 has also been created by TI. Labeled PMP10595, it provides a single-output DC/DC solution with 1.8 V, 2 A output from an input voltage range of 2.7 V to 5.5 V.

Figure 5: Wide VIN input, multi-rail design using Simple Switcher modules LM46002 and LMZ21701.
In conclusion, the four Nano Modules enable the smallest POL and DC/DC converter solutions without compromising performance for a wide range of space-constrained applications. For more information on the synchronous buck controllers and regulators discussed in this article, use the links provided to access product pages on the DigiKey website.
免责声明:各个作者和/或论坛参与者在本网站发表的观点、看法和意见不代表 DigiKey 的观点、看法和意见,也不代表 DigiKey 官方政策。








