LED Drivers for Lighting Control Applications
投稿人:Convergence Promotions LLC
2011-05-27
ROHM offers a number of both external and integrated output LED drivers for a wide range of applications.
The usage of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) is increasing for many reasons. Compared to incandescent lighting, LEDs are more efficient, smaller in size, have a substantially longer life, allow considerably greater design freedom for improved esthetics, and more. In addition, the color of LED lighting is more natural, making it a preferred choice for illumination. The ease of controlling LEDs also makes them natural choices for intelligent lighting systems that adjust based on sensor inputs. An essential aspect of the control is the power management provided by IC drivers.
LED driver capabilities
LEDs require a constant current to produce consistent lighting. Consequently, this forms the basic operating requirements for an LED driver. The accuracy of the current source determines its customer appeal. Current fluctuations can occur with voltage supply variations, and must be avoided. Linear regulators provide a simple control and do not require electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters. However, their power dissipation can become excessive for higher power applications. Buck dc-dc converters are commonly used as the next step up from a linear regulator.
When the driver must control several LEDs in series, a boost converter topology is used. In some cases, a buck-boost topology provides the capability to address a variety of application requirements, including the ability to handle voltage extremes.
LED drivers can be designed to offer a combination of series and parallel LED control. Devices with this capability built-in provide circuit designers the flexibility to control LEDs in different applications with a single driver, rather than requiring different devices that increase qualification testing. Dimming the light level is a common requirement for lighting. However, there are applications for brighter than normal requirements from the same LEDs. In some cases, lighting design may be able to address both situations with the same LEDs with the right LED driver.
Discrete versus integrated LED outputs
A power IC process with analog, digital, and power circuitry allows device designers to integrate the LED power switches with the control circuit, as long as the package can dissipate the power. Integrated LED switches reduce the number of components, saving board space and simplifying inventory and manufacturing. As power levels increase — such as in LED drivers for high brightness (HB) LEDs or when the option for driving LED arrays is desired — a driver or pre-driver that controls external discrete output devices provides flexibility with the output switches selected based on the circuit requirements. As a result, a single LED driver can cover several applications.
ROHM Semiconductor LED driver solutions for lighting control applications
ROHM Semiconductor has highly-integrated LED driver solutions for a variety of lighting control applications. Drivers have integrated switches or, in some cases, pre-drivers designed to switch external power MOSFETs. Three products demonstrate the different approaches that are provided.
ROHM Semiconductor's BD8119FM-M is a four-channel constant current backlight LED driver for medium to large displays, such as those in automotive navigation or dashboard panels. The driver uses an original current mode, buck-boost dc-dc converter and requires only a single coil for simplified design. It is packaged in an 18.5 x 9.9 x 2.31 mm HSOP-M28. The BD8112EFV-M is a two-channel version, suitable for backlighting small to medium size TFT displays, for example, the TFT installed in the instrument cluster. It is offered in an HTSSOP-B24 package. The flexible buck-boost LED drive is shown in Figure 1. It has external PWM control and voltage control of the VDAC terminal for brightness control.
Operating from a supply voltage of 5 to 30 V, the switching frequency of the BD8112EFV-M and BD8119FM-M can range from 250 to 550 KHz, with an external synchronization option to avoid EMI problems with nearby sensitive circuits. A total of 28 LEDs from a 7 x 4-channel matrix can easily be driven by the BD8119FM-M driver with a maximum current of 150 mA per line, and even more with properly configured external circuitry. The driver has built-in LED abnormal state detection for open and shorted conditions as well as built-in protection functions including under voltage lockout (UVLO), overvoltage protection (OVP), thermal shutdown (TSD), overcurrent protection (OCP), and short circuit protection (SCP).
ROHM Semiconductor's BD8105FV and BD8115F fully-integrated drivers provide serial and parallel control. The units require only a few external components, minimizing board space. The BD8105FV consists of twelve open-drain outputs (see Figure 2) and the BD8115F has eight open-drain outputs. The maximum dc current for each output is 50 mA, with a pulsed maximum value of 150 mA.
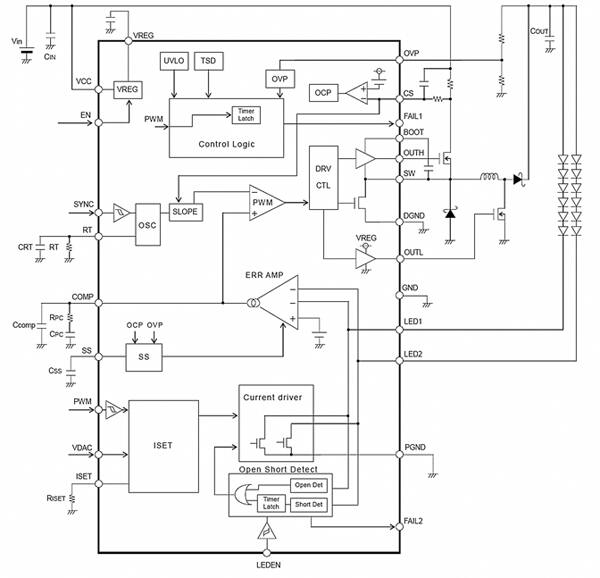
Figure 1: The highly-integrated BD8112EFV-M can drive 150 mA through two LED lines and requires a minimal number of external components.
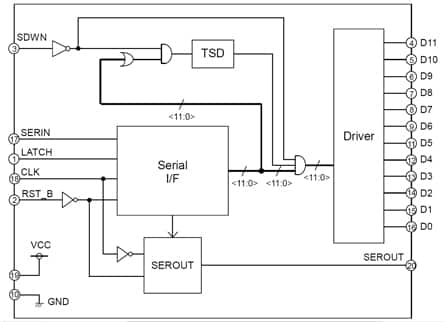
Figure 2: The block diagram of the BD8105FV shows the twelve drain connections to the internal power MOSFETs.
The drivers can have at least two devices cascaded in series as shown in Figure 3, so that more LEDs can be controlled without increasing the number of I/O pins of the microprocessor. Packaged in an SSOP-B20W, the devices have thermal shut-down (TSD) circuitry (nominal detection point at 175°C) built-in to prevent overheating. Since the power devices are integrated in the IC, the TSD circuitry can protect the twelve outputs from excessive temperature.
ROHM Semiconductor's newest LED driver is the BD8381EFV-M for driving multiple HB LEDs. The BD8381EFV-M is a white LED driver with the capability of withstanding high input voltage (50 V max). As shown in Figure 4, a current-mode, buck-boost dc-dc controller is integrated to achieve stable operation over varying voltage input and remove the constraint of the number of LEDs connected in series.
The BD8381EFV-M provides dimming by either a built-in PWM or linear control. Operation with or without a microcomputer is possible.
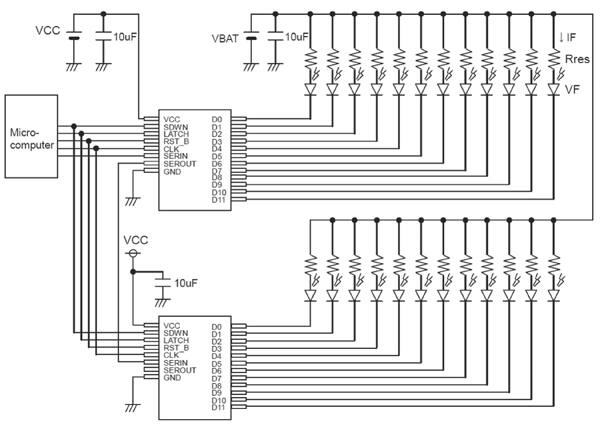
Figure 3: Application circuit for two cascaded BD8105FVs being controlled by a microcomputer with a four-wire (three-line plus enable) I/F serial input.
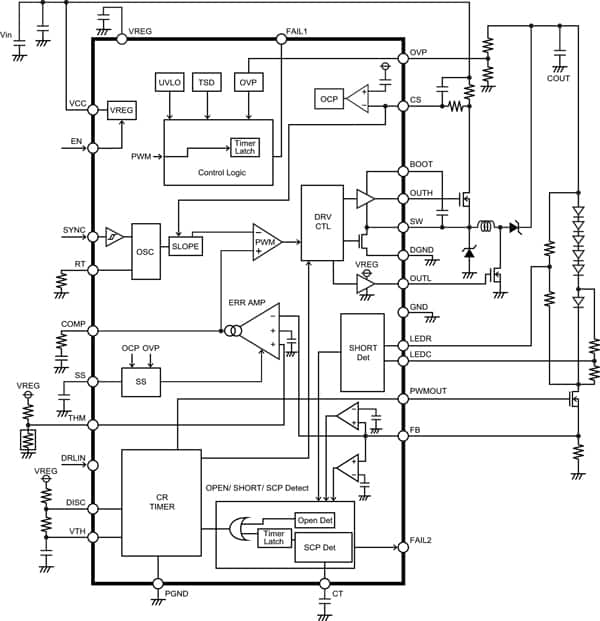
Figure 4: The BD8381EFV-M uses external power MOSFETs so designers can select the switch rating they need for the particular application.
The operating frequency can be set internally between 100 to 600 KHz, or externally synchronized from the internal oscillator frequency up to 600 KHz. Built-in protection functions include UVLO, OVP, TSD, OCP, and SCP with LED error status detection function for OPEN/ SHORT circuit. The circuitry is housed in a HTSSOP-B28 package.
ROHM Semiconductor LED drivers
With the introduction of the BD8381EFV-M white LED driver IC, ROHM Semiconductor has significantly extended its range of highly integrated LED driver ICs. These LED drivers provide designers a variety of design options with integrated or externally switched outputs, parallel/series control, and extensive protection and fault detection functions in small surface mount packages. For more information about the expanding portfolio of LED drivers in ROHM Semiconductor's power management portfolio, visit DigiKey's Lighting Solutions TechZoneSM.

免责声明:各个作者和/或论坛参与者在本网站发表的观点、看法和意见不代表 DigiKey 的观点、看法和意见,也不代表 DigiKey 官方政策。





