温控器的导线类型、应用和接线技术综合指南
2024-12-26
在住宅和商业环境中,温控器接线在暖通空调系统(供暖、通风和空调)的控制和自动化方面具有举足轻重的作用。 本文将探讨常见的温控器电线类型,特别是 2 芯、3 芯、4 芯、5 芯、6 芯、8 芯和 10 芯温控器导线。我们将研究线芯材类型的差异、与各种温控器的兼容性以及为有效控温而推荐的接线技术。此外,还将介绍 O/B 接线的作用以及接线前的基本准备工作。本文旨在通过详细介绍温控器导线,为暖通空调专业人员、电工和 DIY 爱好者提供技术指导。
什么是温控器导线?
温控器导线是一种低压电缆,线径通常在 18 AWG 到 24 AWG 之间不等,用于为暖通空调系统提供信号连接。与电源线不同,温控器导线上不带高电压,而是在温控器和暖通空调系统之间传输控制信号。这些导线是绝缘的,通常以不同的芯线配置进行绑扎,以实现各种功能,例如为温控器供电、控制加热和制冷设备以及操作风扇。
温控器导线的类型:芯线差异及应用
Syston 温控器导线的芯数直接影响其功能以及与不同温控器的兼容性。以下是常见的温控器导线类型及应用的详细介绍:
2 芯温控器导线(图 1)
- 功能:主要用于基本的加热系统
- 应用:适用于无需冷却或风扇控制的简单系统。双芯线通常包括“R”线(电源)和“W”线(加热)。
- 局限性:缺乏用于控制冷却系统或更复杂的暖通空调设备的多功能性。只有加热功能的单极系统的理想选择
 图 1:典型的双芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
图 1:典型的双芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
3 芯温控器导线(图 2)
- 功能:增加一条公共 (C) 导线,用于连续供电
- 应用:通常用于需要为数字温控器供电,但只控制加热的系统。适用于需要基本电源的智能温控器
- 接线:由“R”(电源)、“W”(加热)和"C" (公共)组成
- 局限性:无制冷或风扇控制功能,仅限于基本加热应用
 图 2:典型的 3 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
图 2:典型的 3 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
4 芯温控器导线(图 3)
- 功能:适用于加热和制冷系统
- 应用:4 芯导线包括“R” (电源)、“W” (加热)、“Y”(制冷)和“G” (风扇)。这种配置通常用于需要加热和制冷功能的基本暖通空调系统。
- 局限性:仅限于简单的两级系统;不支持额外的风扇转速控制或分区等高级功能
 图 3:典型的温控器 4 芯电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
图 3:典型的温控器 4 芯电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
5 芯温控器导线(图 4)
- 功能:增加一根公共 (C) 导线,用于在控制加热、制冷和风扇的同时持续供电
- 应用:与需要为 Wi-Fi 和其他智能功能持续供电的更先进温控器配合使用。适用于同时支持解热和制冷的基本暖通空调系统
- 接线:"R" (电源)、"W" (加热)、"Y" (制冷)、"G" (风扇)和"C" (公共)。
- 局限性:通常用于单级系统;不支持多级或多分区设备
 图 4:典型的 5 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
图 4:典型的 5 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
6 芯温控器导线 (图 5)
- 功能:用于具有其他控制要求的高级系统
- 应用:除标准连接(R、W、Y、G)外,6 芯导线还可包括“C”(用于持续供电的公共导线)和辅助导线,如“O/B”,用于控制加热泵。
- 局限性:支持更复杂的设备,但对于多分区或多级系统可能仍然缺乏灵活性
 图 5:典型的 6 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
图 5:典型的 6 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
8 芯温控器导线 (图 6)
- 功能:适用于复杂的多级暖通空调系统
- 应用:包括两级加热(W1 和 W2)和制冷(Y1 和 Y2)的连接,以及风扇导线、电源导线和公共导线。这种导线非常适合需要精确温度控制的多级系统
- 局限性:由于复杂性增加,不常用于住宅环境
 图 6:典型的 8 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
图 6:典型的 8 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
10 芯温控器导线 (图 7)
- 功能:专为最先进的暖通空调系统设计
- 应用:该导线包含 10 根芯线,可支持多个加热和制冷阶段、辅助加热、紧急加热和多种风扇速度等附加功能。这种导线用于先进系统,尤其是大型商用暖通空调设备中
- 局限性:很少用于标准的家用暖通空调系统,因为需要兼容型高级温控器和复杂的暖通空调设备
 图 7:典型的 10 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
图 7:典型的 10 芯温控器电缆。(图片来源:Syston)
什么是 O/B 导线?
O/B 导线通常被称为换向阀导线,对于热泵系统至关重要(图 8)。O/B 导线用于控制热泵中的换向阀,换向阀决定系统处于加热还是制冷模式。在制冷模式下,O/B 导线通电,使转向阀转向以允许制冷;在加热模式下,O/B 导线断电。该导线通常与温控器的 O/B 端子连接,具体设备视制造商提供的技术规格而定。
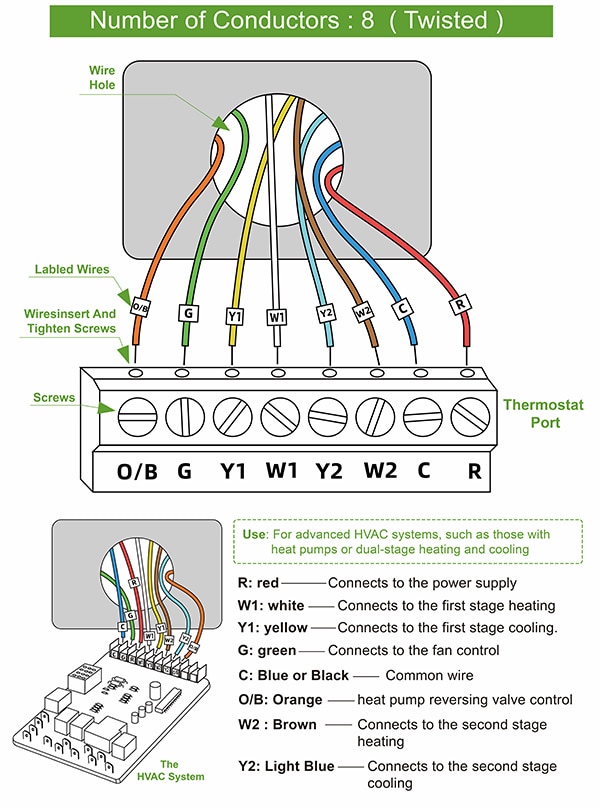 图 8:热泵温控器的接线名称。(图片来源:Syston)
图 8:热泵温控器的接线名称。(图片来源:Syston)
温控器接线的应用
温控器接线对以下暖通空调组件至关重要:
- 供暖:控制加热装置,如火炉和热泵
- 制冷:管理制冷设备,包括中央空调
- 风扇:控制风扇的速度和工作模式,实现有效的空气流通
- 暖通空调系统:将加热、制冷和通风集成到一个控制单元中,实现无缝气候管理
温控器导线对于管理这些组件至关重要,可帮助用户保持理想的室内环境并提高能效。
如何使用温控器接线控制制冷、加热、风扇和暖通空调系统
制冷:要控制冷却系统,需将“Y”线从自动调温器连接至 HVAC 制冷装置。当室内温度高于设定值时,温控器将启动制冷系统。
加热:将“W”导线与加热装置连接。当温度降至所需水平以下时,自动调温器发出信号,启动加热系统。
风扇控制:“W”导线用于控制风扇运行。温控器可以控制风扇速度(如支持),以保持空气流通稳定,确保冷、热空气均匀分布。
热泵系统:对于热泵配置,O/B 导线控制换向阀,使系统在加热和制冷模式之间切换。这种设备常见于气候温和的地区,热泵在这些地区能有效地发挥作用,保持全年舒适。
准备温控器接线
在温控器接线之前,请按照以下准备步骤操作:
断开电源:确保在开关箱处断开电源,避免触电。温控器线路的工作电压较低,但出现意外短路仍会损坏设备。
检查兼容性:确认温控器和暖通空调系统与所用的温控器导线兼容。并非所有温控器都支持多级接线,有些温控器可能没有额外芯线连接。
收集工具:准备剥线器、螺丝刀和电工胶带等工具。万用表也有助于测试连接和确保接线正确。
识别端子:在断开连接之前,根据每根导线的功能(如 R、W、Y、G)为其贴上标签。这一步骤在升级或更换现有温控器时尤其有用。
请参考接线图:请务必参考温控器手册和暖通空调接线图,以确保连接正确。接线不正确会导致系统故障或损坏。
结论
Syston 温控器接线是设置和运行暖通空调系统的基本组成部分。了解芯线类型的不同--从用于简单加热的 2 芯线到用于高级多级设备的 10 芯线,可以让技术人员和业主根据自己的具体需求选择正确的电线类型。O/B 导线在热泵系统中起着至关重要的作用,可使用户在加热和制冷模式之间有效切换。
用户只需执行正确的接线技术并了解每个温控器和暖通空调组件的具体要求,就能在各种环境中实现高效的气候控制。确保兼容性、适当的准备工作和准确的接线,将有助于实现暖通空调系统的最佳性能,达到其最长使用寿命。
免责声明:各个作者和/或论坛参与者在本网站发表的观点、看法和意见不代表 DigiKey 的观点、看法和意见,也不代表 DigiKey 官方政策。






